-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is a Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP)? Explained!
- Author:Diksha Bhandari
- Read Time:9 min
- Published:
- Last Update: July 4, 2024
Table of Contents
Toggle
Want to know what a travelling salesman problem (TSP) is? Need solutions to real-life TSP challenges. Learn here.
Table of Contents
ToggleDo you also look for the shortest route on Google Maps before embarking on a trip?
I am sure, you know multiple routes to reach the office, the mall, or your desired location, but checking on the internet before leaving home has become a ritual. It becomes all the more important to refer to maps when you have to pick up friends or colleagues along the way.
‘ADD STOPS’
Yes, you are right! 💯
That’s what solving the TSP challenge using software means!
What is a Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP)?
The traveling salesman problem is the popular combinatorial optimisation challenge in mathematics and computer science. The prime objective of the problem is to determine the shortest possible route a salesperson must take to cover a set of locations in one go and then return to the starting point.
Addressing travelling salesman challenges and their optimisation are more relevant in this time and age, especially in the supply chain, logistics and delivery space.
TSP may result in delayed deliveries and slimming profits as it’s not easy for delivery agents to choose the most viable and cost-effective route in real-time.
💡Backgroud of Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP)The Traveling Salesman Problem originated in the 1930s. It was first formulated as a mathematical challenge, aiming to find the shortest path for a salesperson to visit a combination of places. Its computational complexity has led to the development of numerous algorithms and heuristics, making it a cornerstone problem in optimization theory and a vital tool for businesses seeking to minimize travel costs and improve efficiency. |
What are Traveling Salesman Problem Challenges to Solve?
When a salesperson is in the field hopping from one client site to another, finding out the best and the shortest route is an added pressure on the agent. In today’s day and age, distance isn’t the only factor that defines efficiency. There are several factors, such as time, fuel consumption, capacity, etc. that together define efficiency.
However, addressing the travelling salesman challenges involves mitigating a few unavoidable challenges along the way that field agents face themselves.
1. Time Constraints
Sales agents often have a tight schedule with multiple deliveries to make with a short TAT. Similarly, in TSP, optimising routes to minimise travel time is a fundamental challenge.
2. Last-minute Changes
Eleventh-hour changes are not a new concept for salespeople. They encounter urgent visits and last-minute cancellations a lot. Similarly, TSP solutions must be adaptable to handle dynamic scenarios and route modifications.
3. Resource Efficiency
Just as salespersons aim at reducing fuel costs and ensuring on-time deliveries, TSP solutions such as TrackoMile must strive for resource optimisation by reducing travel distances and delivery TAT.
4. Objective Diversification
While solving the travelling salesman problem (TSP), optimising multiple objectives such as cost, time, and environmental factors adds complexity as solutions need to balance conflicting goals.
5. Combinatorial Complexity
TSP is a combinatorial optimisation problem, which means it involves complicated mathematical calculations with numerous variables. Sometimes, complex scenarios get further intricate as multiple variables are involved.
6. Adaptability and Scalability
Similarly, how sales agents adjust to the routes on the fly, the route algorithm must be flexible and responsive to real-time changes such as spiking volumes, vehicle breakdown or traffic slow down. A TSP solution must have a good appetite to handle large datasets and complex networks.
Also Read 4 Key Solutions for Fuel Management System 2023
Top 5 Solutions to The Travelling Salesman Problem
The traveling salesman problem solutions offer various trade-offs between computational intricacies and the quality of the resolution, allowing practitioners to choose the best-suited approach based on their needs and problems.
Here are the Top 5 solutions to the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP):
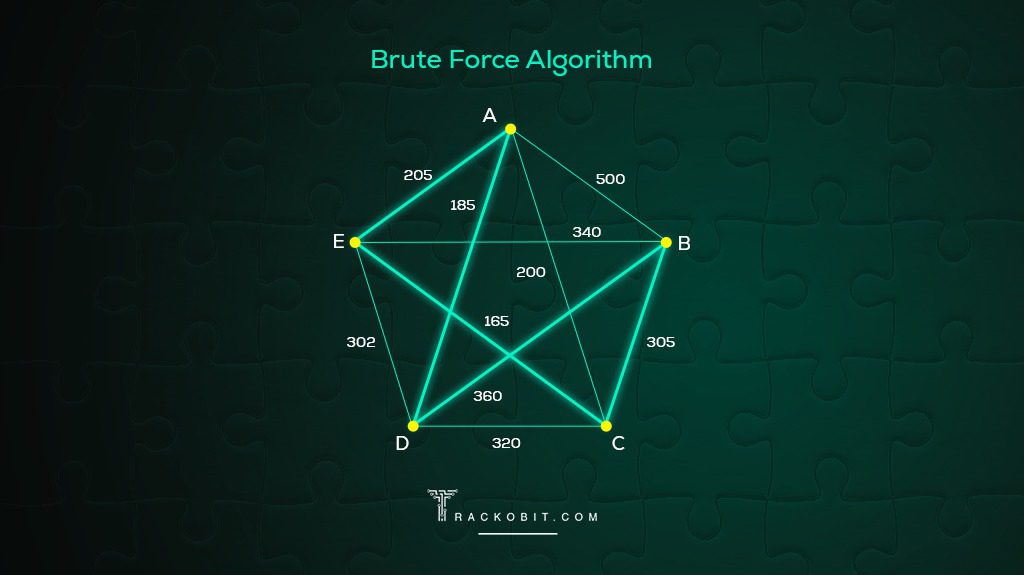
1. Brute Force Algorithm
The Brute Force algorithm is a straight approach to solving the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP). It systematically explores all possible routes to identify the shortest one among them all. While it guarantees an optimal solution, its downside lies in its major time complexity, making it practical only for small TSP challenges.
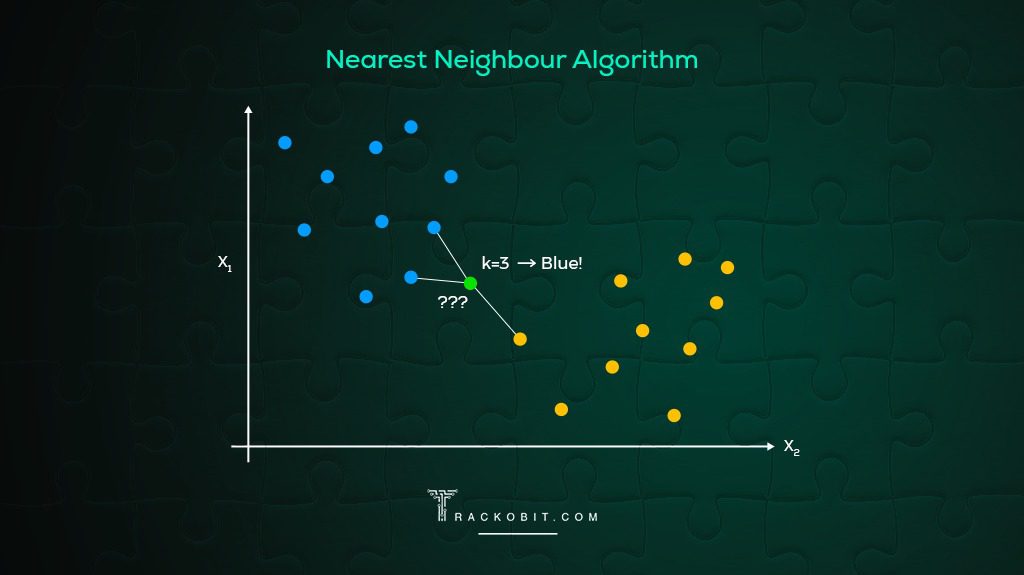
2. Nearest Neighbour Algorithm
The Nearest Neighbour method is the simplest heuristic for the TSP. It starts from the first location and repeatedly selects the closest unvisited location to form a tour. Although it is quick to implement this method, it may always yield the optimal solution for it prioritises proximity over other factors.
💡Heuristic Definitionnoun |
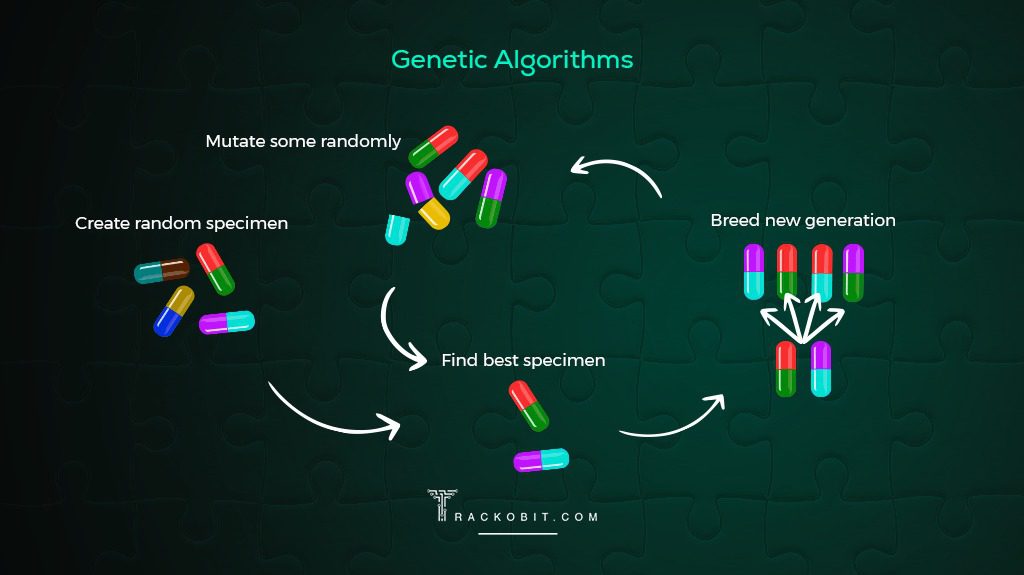
3. Genetic Algorithm
This technique or method draws inspiration from nature itself. They evolve TSP solutions through selection, crossovers and mutation. They pick the best routes and mix them up. This creates new routes that might be even better. Then, they keep the best ones and repeat the mixing and picking process. Survival of the fittest in the true sense.
4. Ant Colony Optimisation (ACO)
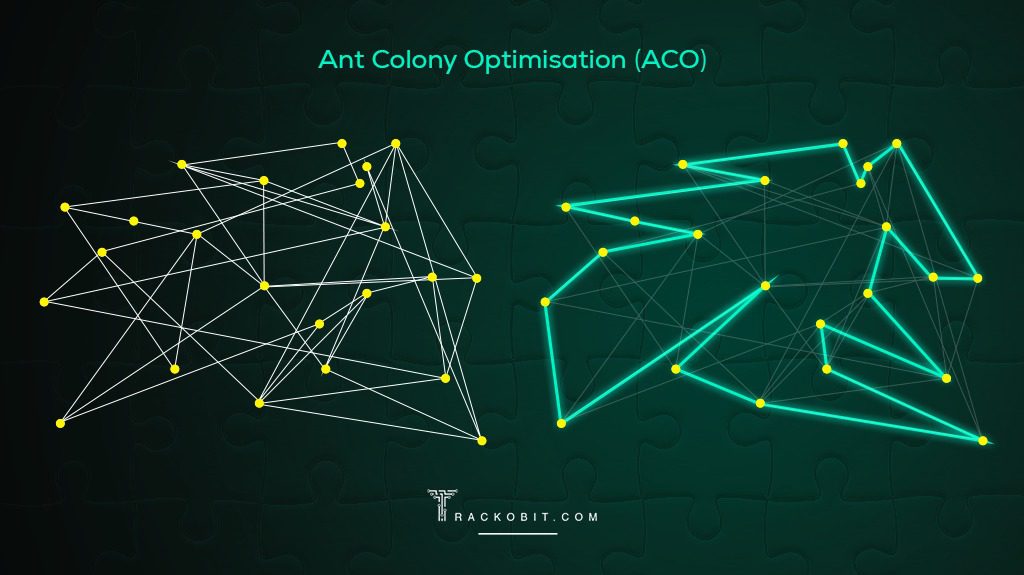
Ants have a tendency to leave pheromones on the shorter routes they find, calling fellow ants on the same route. They keep leaving more pheromones on the shorter routes they find. Over time, the collective behaviour of the ants causes them to converge on the shortest route. Inspired by the nature of ants, ACO finds the shortest route by analysing the trails of data left by artificial ants based on the strength of these data trails.
5. Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Programming is like solving a puzzle, step-by-step, by breaking it into smaller pieces. In TSP challenges, it finds the best route to visit all locations. It begins with figuring out the shortest route between two locations; then it builds on that to find ways to more locations. It’s a smart TSP solution for small scenarios but may require significant memory resources for larger and more complex problems.
What Are Real-world Travelling Salesman Problem Applications?
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) has a wide array of applications across various domains due to its relevance in optimising routes and sequences. Here are several crucial real-word TSP applications and implementations in the real world.
1. TSP implementation in Logistics and Delivery Services
The logistics and supply chain sectors have the widest TSP applications.
- Courier, Express & Parcel: Companies like FedEx, UPS, and DHL rely on TSP algorithms to optimise delivery routes for their fleet of delivery trucks. By finding the most efficient sequence of stops, they minimise fuel consumption, reduce delivery TAT, and save on operational overheads too.
- On-demand Delivery: Food delivery companies, instant grocery delivery apps and at-home appointment platforms like Swiggy, BlinkIt and UrbanCompany, respectively, leverage TSP solutions to ensure timely delivery. Enhancing the customer experience and increasing the number of deliveries each rider can make.
2. TSP Applications in Transportation and Urban Planning
Waste collection routes, Traffic light synchronisation, optic cable installation, etc. are some areas where TSP Solutions works like a knight in shining armour. Other real-world TSP applications include
- Public Transport: City planners and public transport agencies use TSP principles to design bus, tram and train routes that reduce travel for passengers.
- Emergency Service Dispatch: Ambulance services, Police PCR vans employ TSP algorithms to dispatch vehicles quickly and efficiently in response to emergency calls. Finding the shortest route to reach the incident location can save lives.
- Urban Mobility Solution: In the era of ride-sharing and on-demand mobility apps like Uber, Ola, Lyft, etc., real-world TSP applications become prominent. TSP solutions optimise the route to destinations, ensuring quick and cost-effective transportation.
Other significant real-life applications of the Travelling Salesman Problem are
- TSP in Healthcare and Medical Research – for DNA sequencing and understanding genetic patterns and diseases.
- TSP in Manufacturing and Production – In circuit board manufacturing and job scheduling of technicians.
- TSP in Robotics and Autonomous Vehicles -Self-driving cars and drones use TSP-like algorithms for efficient navigation.
Solving the Travelling Salesman Problem – Last Mile Delivery Route Optimisation
Route optimisation is the key to efficient last-mile delivery. In order to attain flawless route optimisation, the software must solve the traveling salesman problem every step of the way.
Why it’s essential to solve TSP for Last Mile Delivery?
In simple and minimal words, solving TSP problems helps in many ways:
- Saves Time: It makes deliveries faster, so your customers get orders sooner.
- Customer Satisfaction: Fast deliveries give you an edge over the competition and enhance customer experience too.
- Saves Money: It reduces fuel wastage and vehicle wear, making deliveries cheaper.
- Environment Friendly: It lowers pollution by using fewer vehicles and shorter routes.
- Happy Staff: Drivers and dispatchers have less stress and can finish their work faster.
How do we solve the travelling salesman problem for last-mile delivery?
Solving TSP challenges for Last-mile delivery is like solving a big jigsaw puzzle. There are a hundred thousand addresses to visit daily. The software must find the shortest and most optimised route to them and come back to the starting point at the end.
- Our route optimisation software, TrackoMile, leverages capacity management, routing algorithms and robust rule engines to present the most optimal combination of delivery addresses. Thereby giving the most optimally planned routes or trips.
- All delivery managers have to do is upload the CSV file of the addresses or integrate TrackoMile to their CRM to fetch the delivery addresses. Now trip allocation, route optimisation, dispatch and everything else happen in a few clicks.
- ETA when the delivery is en route, POD when the order is delivered successfully, and trip analysis, are added features to simplify overall operations.
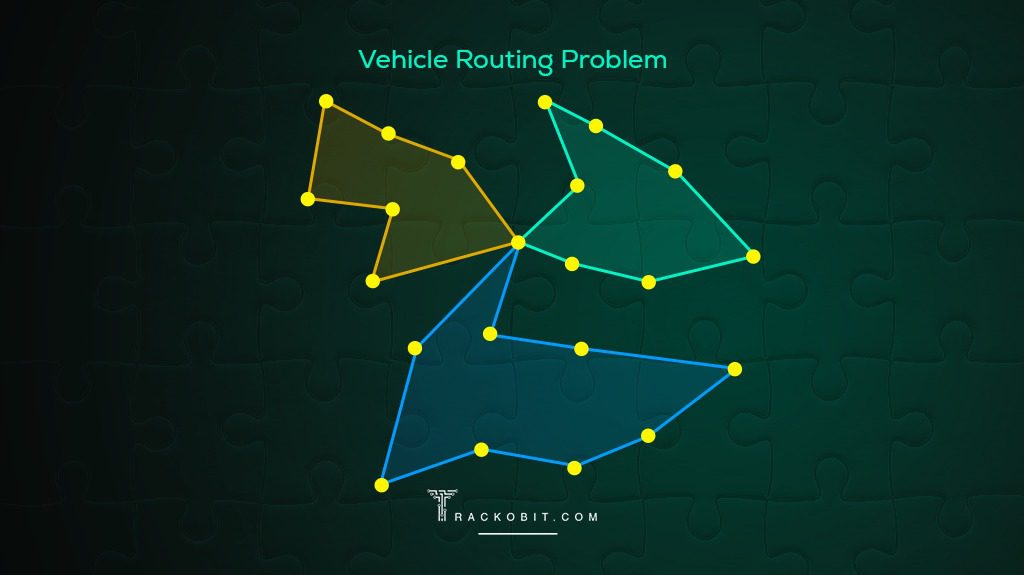
What is a Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP)?Optimizing routes for multiple vehicles to deliver goods to various customers while reducing total distance, time and cost. |
The Vehicle Routing Problem is very similar to TSP, with wide applications in logistics, delivery services and transportation. While TSP focuses on finding the shortest route for a single traveller visiting various locations, VRP deals with multiple vehicles serving multiple customers, considering added constraints like vehicle capacity, TATs and more.
How Can AI Help in Solving Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)?
AI or Artificial Intelligence are becoming the driving force for business growth across various industrial sectors. AI particularly aids in solving the Traveling Salesman Problem(TSP) in the logistics and delivery sector by employing advanced algorithms and techniques. What are a few tricks up AI’s sleeves that help in automating TSP resolution? Let’s find out!
1. Advanced Algorithms
AI algorithms such as Genetic Algorithms, ACO, simulated annealing and a few others mentioned above, tackle complex Travelling Salesman Problem scenarios.
2. Machine Learning
Gathering information from historical data and optimising routes based on real-time insights is what AI is best for. Machine learning models are trained to adapt to changing conditions, like traffic, weather and delivery constraints, to provide a more accurate plan of action.
3. Parallel Computing
AIi enables the use of a parallel computing process, which means solving multiple segments of TSP simultaneously. This accelerates the problem-solving process for large-scale challenges.
4. Heuristic Improvement
TSP Heuristics powered by AI can groom initial solutions, gradually improving their results over time. These heuristics can be applied iteratively by AI to reach better results.
5. Hybrid Approaches
Applying hybrid algorithms is not a new technique to refine techniques and produce more accurate results. AI on top of it singles out data-oriented combinations that work the best in varied use cases.
Wrapping Up!
The travelling salesman problem’s importance lies in its real-world applications. Whether optimising delivery routes, planning manufacturing processes or organising circuit board drilling, finding the most efficient way to cover multiple locations is crucial to minimise costs and save time.
The TSP problems have evolved over the years, and so have TSP algorithms, heuristics and solutions. With the advent of advanced technologies such as GPS and machine learning, TSP continues to adapt and find new applications in emerging fields, cementing its status as a fundamental problem in optimization theory and a valuable tool for various industries.
Mobility automation software like Trackobit, TrackoMile and TrackoField resort to TSP heuristics to solve challenges along the way.
Read Blog – Best Delivery Route Planner Apps for 2023
Traveling Salesman Problem FAQs
-
What is TSP?
TSP is an abbreviation for Traveling Salesman Problem. It’s the routing problem that deals with finding the shortest route to travel to a combination of locations in the most optimal manner.
-
Is Travelling Salesman Problem Solvable?
Yes, the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is solvable, but the time to find the solution can grow proportionately with an increase in the number of locations. With the evolution of travelling salesman problem applications, various TSP algorithms and heuristics, their hybrids have also emerged.
-
Wh at is the objective of TSP?
The objective of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is to find the shortest possible route that covers all given locations or waypoints and comes back to the starting point with the least resource utilisation.
Diksha Bhandari is the Content Marketing Manager at TrackoBit. With over a decade of experience in the media and advertising industry, she has transitioned her expertise to the world of software and t... Read More
Related Blogs
-

What is an End-User License Agreement (EULA)?
Tithi Agarwal August 29, 2024EULA, or End-user license agreement, we all know, is a legal agreement granting users a software license and how it…
-

GPS vs NavIC: Global Reach vs. Regional Precision
Anvesha Pandey July 30, 2024Want to know what’s better, GPS or NavIC? This piece of writing will surely give you clarity on all the…
-

What is NavIC- India’s Homegrown GNSS System
Anvesha Pandey July 23, 2024Have you heard of NavIC – YES India’s very own GPS tracking system! This piece of writing is all about…
-
Top 12 Google Map Alternatives – Offering Precise Navigation
Nandita Gupta December 11, 2023Explore our best picks for 12 free Google map alternatives that offer accurate and secure location and navigational solutions.

Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.