-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is NavIC- India’s Homegrown GNSS System
- Author:Anvesha Pandey
- Read Time:10 min
- Published:
- Last Update: December 23, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
Have you heard of NavIC – YES India’s very own GPS tracking system! This piece of writing is all about the Indigenous Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS).
Table of Contents
Toggle
For decades, India relied on foreign navigation systems, but now we can see some changes going all around. Well, it was 2013, when India unveiled its own Indigenous Global Navigation Satellite System named NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation).
Before the basics i.e.unfolding NavIC, let’s just appreciate this monumental feat in the nation’s technological journey that is just not confined to being accurate and robust but is also a self-reliant positioning system built especially for the needs of India.
So together, let’s just dive into the details of NavIC – from its history to the future, the every in and out.
Basics first!
What is NavIC?
The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) aka NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) is a group of 7 satellites developed by ISRO. This system provides a Global Positioning System (GPS) service in India. It provides real-time positioning and timing services. The system covers areas from India extending up to 1500 kms and is expected to reach more areas in the future.
NavIC consists of 7 satellites i.e. (IRNSS- 1B, IRNSS- 1D, IRNSS- 1E, IRNSS-1F, IRNSS-1G, IRNSS-1I) orbiting Earth to provide accurate positioning and timing information.
Now that we know the definitions and the constellation of satellites, let’s quickly unfold what all the systems provide us with.
Well, NavIC provides us with various services such as Standard Positioning Service (SPS) for civilian use, Restricted Services (RS) for authorized users like defense forces, and a Search and Search and Rescue service.
A Fun Fact:- The word NavIC is derived from the Sanskrit word Navik, which means sailor or navigator.
📌Also Know About GPS: What is GPS and How Does GPS Work?
How Does NavIC Work?
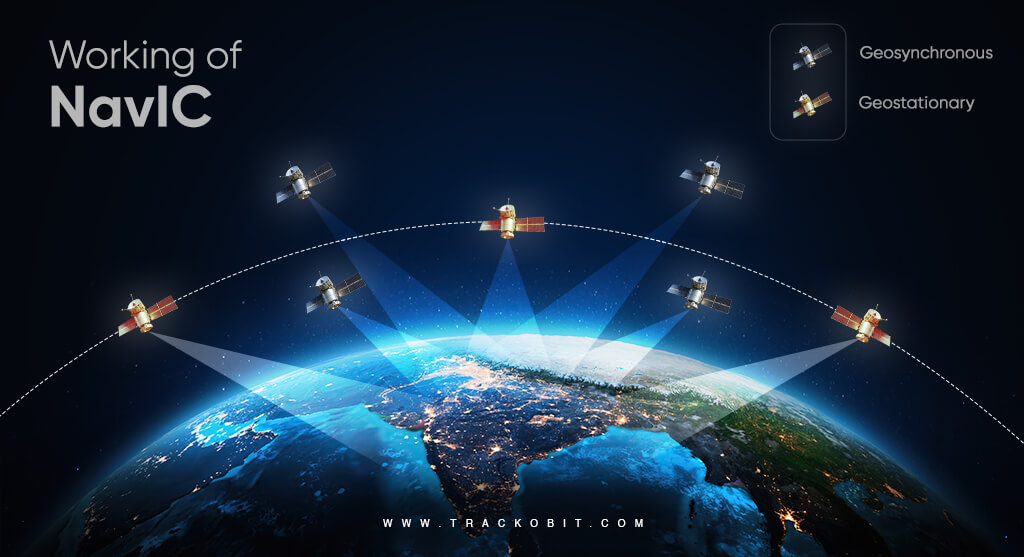

To understand how NavIC works, we have to split the working of the GNSS system into three segments – the space segment, the ground segment, and the user segment.
SPACE SEGMENT
This part involves satellites in space. The space segment consists of a constellation with 7 satellites. From which 3 are (Geostationary) and 4 (Geosynchronous orbit).
Sounds complex? Let us explain to you briefly about geostationary and geosynchronous satellites.
Geostationary Orbit (GEO) refers to an orbit where a satellite revolves around the Earth at a rotational speed similar to Earth’s. As a result, the satellite appears to be stationary relative to a fixed point on the Earth’s surface. In NavIC, the satellites in geostationary orbit are-
- IRNSS-1G
- IRNSS-1H
- IRNSS-1I
Geosynchronous orbit refers to an orbit where a satellite has a period equal to the Earth’s rotational period, but these satellites do not necessarily remain fixed over one point on the equator. NavIC has satellites in geosynchronous orbits that provide coverage over the Indian subcontinent and surrounding areas. The geosynchronous satellites are-
- IRNSS-1A
- IRNSS-1B
- IRNSS-1C
- IRNSS-1D
These satellites work together to provide accurate position data, timing, and navigation services, enhancing regional navigation capabilities for civilian and military purposes.
GROUND SEGMENT
Well, the ground segment is responsible for monitoring, controlling, and managing the satellites. It consists of components like control centers, ground stations, and a network of reference stations that play various roles-
Roles of the Control Center-
- The overall management of the NavIC system (satellite operations and maintenance)
Roles of the Ground-
- Monitor the satellite health
- Track their positions
- Ensure the accuracy of the navigation signals.
USER SEGMENT
The design includes the receiver and antennas for capturing the IRNSS signals. The user segment consists of two receiver types-
A single-frequency IRNSS receiver that captures SPS/RS signal at L5 or S-band frequency and is capable of making ionosphere corrections.
A dual-frequency IRNSS receiver that captures SPS/RS signals at both L5 and S-band frequencies, allowing it to track multiple radio signals from different satellites with various signals.
Now that you know what exactly is NavIC and how these seven sisters of satellites work, let us tell you a story about how NavIC was developed.
Read Blog – Top 10 Navigation Apps for Android and iOS
| 📌Story Time –
We usually use GPS for tracking, but India made NavIC to become more independent with their satellite navigation. India wanted its own system because, in crucial situations, it might not always be possible to rely on systems controlled by other countries. For eg:- Back in 1999, the Indian military faced challenges while seeking GPS data during the Kargil conflict with Pakistani troops. The US government’s refusal to grant access to its space-based navigation system highlighted the necessity for India to have its own indigenous satellite navigation system. Following this incident, the Indian government decided in May 2006 to develop its navigation system, reducing its dependency on foreign systems such as GPS or GLONASS. The establishment of NavIC by the Indian Space Research Organisation has provided India with enhanced control over its navigation and timing data, crucial for national security and data integrity. Also, it not only helps improve navigation, disaster response, and farming but also encourages new ideas and technological growth within the country. |
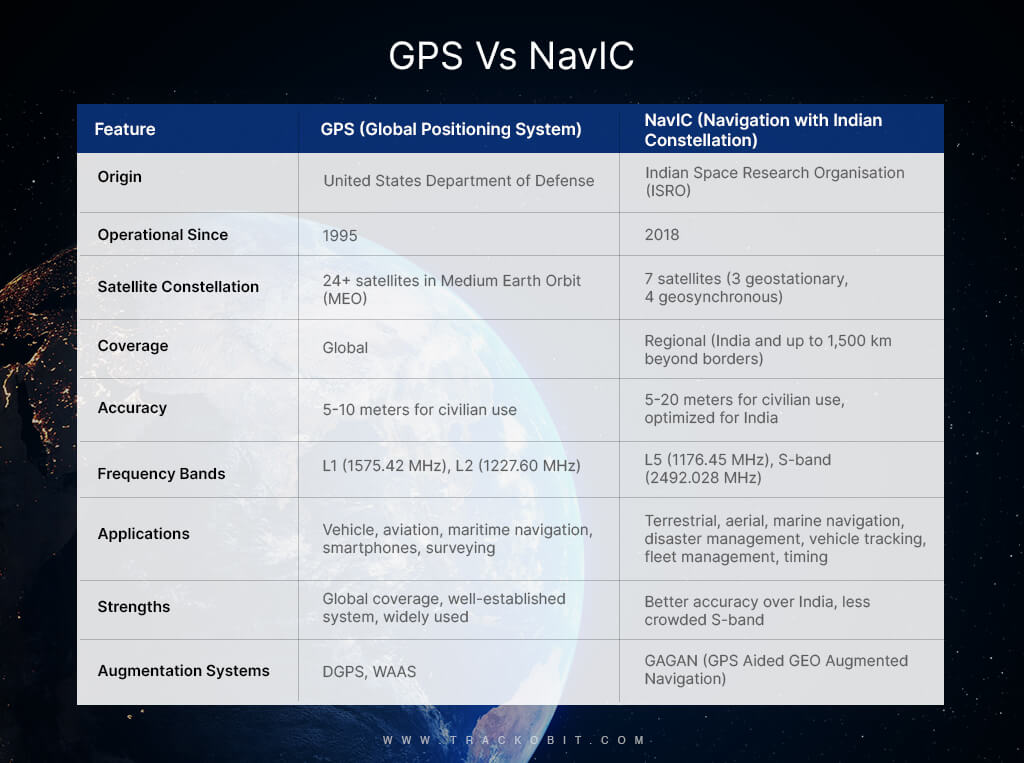
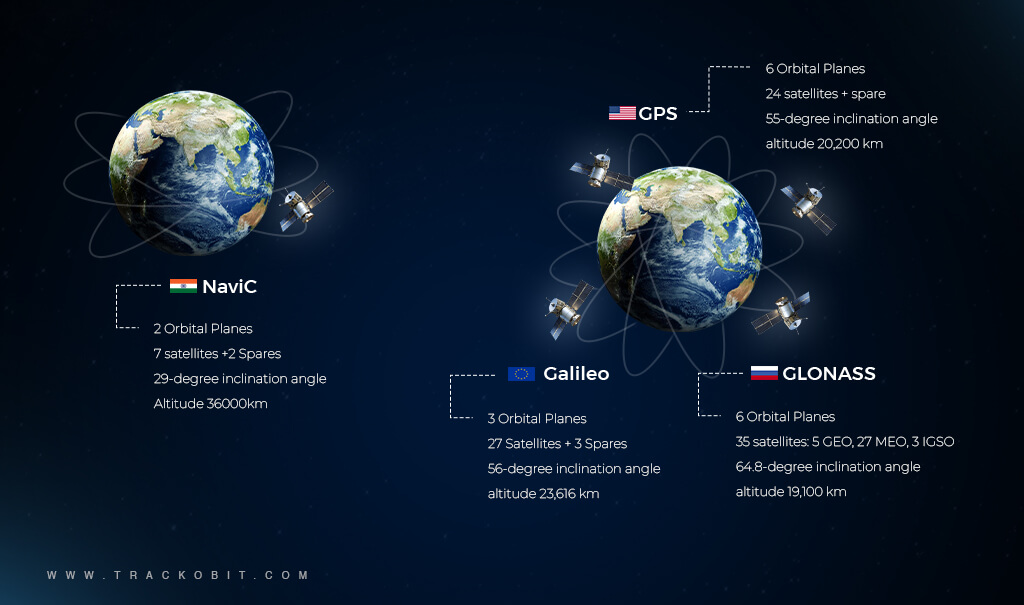
How is NavIC Different from GPS and GLONASS?
IRNSS aka NavIC, GPS, and GLONASS are all satellite-based navigation systems, but they have key differences in terms of their origin, coverage, and capabilities.
1. Origin and Development
a) NavIC
- Developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Designed primarily for regional navigation covering India and the surrounding region.
b) GPS
- Developed by the United States Department of Defense.
- Provides global coverage.
c) GLONASS
- Developed by the Russian Federation’s Roscosmos.
- Provides global coverage.
2. Coverage Area
a) NavIC
- Covers India and an area extending up to 1,500 km around the Indian mainland.
- Aimed at providing accurate position information services to users in India and the surrounding region.
b) GPS
- Provides worldwide coverage.
- Used globally for various applications including navigation, mapping, and timing.
c) GLONASS
- Also provides worldwide coverage.
- Used globally similar to GPS.
3. Constellation and Satellites
a) NavIC
- Consists of 7 satellites in geostationary and geosynchronous orbits.
- Positioned to provide enhanced accuracy over the Indian region.
b) GPS
- Consists of a minimum of 24 satellites in medium Earth orbit.
- Satellites are distributed to ensure global coverage.
c) GLONASS
- Consists of a minimum of 24 satellites in medium Earth orbit.
- Satellites are also distributed to provide global coverage.
4. Accuracy and Performance
a) NavIC
- Claims to provide better accuracy than GPS in the Indian region, with position accuracy better than 20 meters in the primary service area.
- Designed to provide position accuracy of less than 10 meters.
b) GPS
- Generally provides an accuracy of about 5 meters globally, but this can vary based on various factors including receiver quality and environmental conditions.
c) GLONASS
- Offers similar accuracy to GPS, with performance enhancements in northern latitudes due to satellite positioning.
5. Civil and Military Uses
a) NavIC
- Designed for both civilian and military use.
- Includes standard positioning services for civilian use and restricted services for authorized users (e.g., military).
b) GPS
- Widely used in civilian applications including navigation, mapping, and timing.
- Also provides encrypted services for military use.
c) GLONASS
- Used for both civilian and military purposes.
- Civilian signals are open for global use, while military signals are encrypted.
6. Frequency Bands
a) NavIC
- Utilizes L5 and S-band frequencies.
- The dual-frequency operation helps in mitigating errors caused by the ionosphere.
b) GPS
- Primarily operates in L1, L2, and L5 bands.
- Uses a dual-frequency system to enhance accuracy and reduce errors.
c) GLONASS
- Operates in L1 and L2 bands.
- Uses frequency division multiple access (FDMA) to distinguish signals.
Discussing GPS vs NavIC is something we’ll unfold in detail in the future.
ISRO’S NavIC & MapMyIndia’s Collaboration
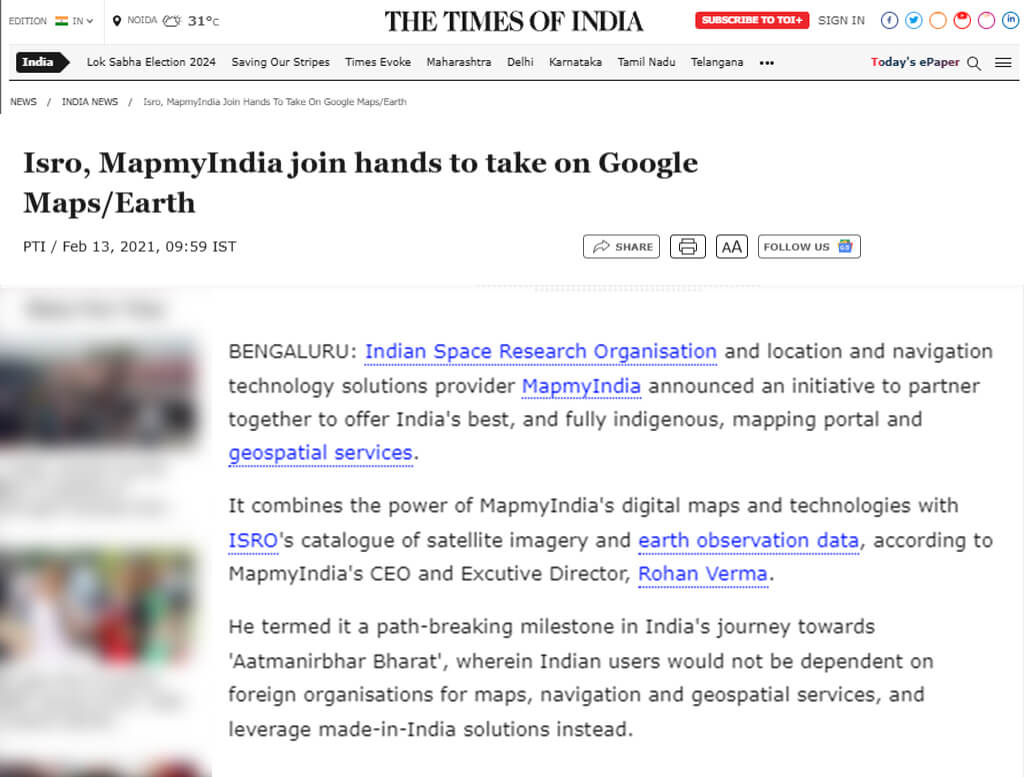
The collaboration between ISRO’s NavIC and MapmyIndia signifies a significant step towards enhancing indigenous navigation solutions in India. This partnership aims to integrate MapmyIndia’s digital maps and navigation services with ISRO’s NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) satellite-based navigation system.
Some of the key aspects that we can see with this collaboration are as follows-
Integration of Services
MapmyIndia has already integrated its digital mapping services with NavIC’s positioning services. This integration aims to provide precise and real-time navigation and location-based services.
Enhanced Accuracy
NavIC is known for its high accuracy in the Indian region. By leveraging NavIC’s satellite data, MapmyIndia is expecting to enhance the accuracy of its maps and navigation services.
Indigenous Technology
The collaboration promotes the use of indigenous technologies, reducing dependency on foreign systems like GPS. It also encourages the development of home-grown solutions for navigation and location-based services.
Sounds amazing right? But just like how a coin has 2 sides, similar to the GNSS system, NavIC also has some cons. Together let’s unfold them.
Major Challenges Faced By NavIC
NavIC, India’s navigation system has been facing some significant challenges that surely have impacted its performance and adoption. Below here we have highlighted some of its significant challenges.
-
Limited Global Coverage
NavIC primarily covers India and its surrounding regions, limiting its global applicability. This makes it less competitive compared to other GNSS systems like GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, which offer worldwide coverage.
-
Compatibility and Integration
Many existing devices and systems are designed to work with established GNSS like GPS. Integrating NavIC into these systems requires additional effort and investment, which can hinder its widespread adoption.
-
Awareness and Adoption
There is a lack of awareness about NavIC among potential users, both domestically and internationally. This results in slower adoption rates and reduced market penetration.
-
Technological Challenges
Maintaining and upgrading the technology infrastructure for NavIC is challenging. This includes ensuring the reliability and accuracy of satellites, ground stations, and user equipment.
-
Funding and Investment
Sustained funding and investment are crucial for the continuous development and maintenance of NavIC. Budget constraints can affect the quality and expansion of the system.
-
Geopolitical Factors
International cooperation and standardization are essential for GNSS systems. Geopolitical tensions can impact collaborations and the integration of NavIC with other global systems.
-
Environmental and Space Weather
Satellite navigation systems, including NavIC, are affected by space weather phenomena like solar flares and ionospheric disturbances. These can degrade signal quality and accuracy.
-
Spectrum Allocation
Efficient spectrum management is critical for GNSS operations. NavIC must navigate spectrum allocation challenges to ensure its signals do not interfere with other systems and vice versa.
What are the Features of NavIC?
NavIC, or Navigation with Indian Constellation offers a range of features that provide vital services not just for India, but for the surrounding regions as well. Here’s a closer look at what makes NavIC stand out.
- Precise Positioning- NavIC highlights high-accuracy positioning information, with an accuracy of better than 10 meters in India and 20 meters in surrounding areas. This makes it ideal for various applications like navigation in transportation (road, air, and marine), agriculture (precision farming), and disaster management (for better help).
- Accurate Timing– IRNSS goes beyond navigation. It offers highly accurate timing signals, crucial for sectors like telecommunications and power grid synchronization. Additionally, precise timing ensures the smooth functioning of these critical infrastructures.
- Enhanced Surveying- Surveying, mapping, and geocoded data collection all benefit from NavIC’s reliable satellite-based positioning. This allows for more accurate measurements and improved data collection for various purposes.
- Emergency Support- During emergencies, NavIC plays a vital role. Its ability to track locations quickly and accurately aids search and rescue operations, potentially saving lives.
- Weather Forecasting- NavIC even contributes to meteorology. By providing atmospheric data, it helps improve weather predictions, leading to better preparedness for weather events.
All in all, NavIC is a versatile system that offers a multitude of benefits for India and its surrounding regions. It will be amazing to watch how well this GNSS will grow in the future.
NavIC in News For Public & Commercial Vehicles
Recently, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) of India has mandated fitting NavIC-based AIS-140 compliant vehicle trackers in all public and commercial vehicles. This move is aimed at improving road safety, monitoring, and management of commercial vehicle operations across the country.
Wondering what’s AIS140 Compliance?
Well, here it is- AIS-140 (Automotive Industry Standard 140) is a set of standards laid down by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) for vehicle tracking systems and emergency request buttons.
Bottom Line from the Bottom of Our Indian Hearts
NavIC, India’s GNSS system is a moment of pride for the country. Now it is high time that we show great support towards our country’s originated system “NavIC” for day-to-day positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services.
NavIC isn’t just a navigation system; it’s a symbol of India’s technological prowess. It empowers citizens, fosters innovation, and paves the way for a more secure and efficient future.
We are all excited to see NavIC in the future offering services for commercial fleet tracking. Well, whenever that happens, you will see TrackoBit‘s fleet management software running in parallel with this technology and offering 99.9% locational updates, better monitoring of driving events, and more precise data for enhanced visibility.
Know how TB can revolutionize fleet management!
FAQs on NavIC or Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System
-
What is NavIC 2.0?
NavIC 2.0 (Navigation with Indian Constellation 2.0) is the upgraded version of India's regional satellite navigation system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It provides accurate position information services to users in India and the surrounding region. The enhancements in NavIC 2.0 include improved accuracy, extended coverage, and additional satellites to ensure better reliability and performance.
-
What is a NavIC app?
The NavIC app is a mobile application developed to leverage the NavIC satellite navigation system. It provides users with location-based services, such as real-time navigation, mapping, tracking, and geospatial information. The app aims to enhance the user experience by offering accurate and reliable positioning data, primarily for users in India and its neighboring regions.
-
List of some other navigation systems?
Some of the well-known navigation systems or GNSS systems are listed below- 1. GPS (Global Positioning System)- Developed and maintained by the United States. It's the most widely used navigation system worldwide. 2. GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System)- Developed by Russia. It serves as an alternative and complement to GPS. 3. Galileo- Developed by the European Union. It aims to provide high-precision positioning services and is interoperable with GPS and GLONASS. 4. BeiDou- Developed by China. It offers global coverage and provides positioning, navigation, and timing services.
Anvesha is a communication specialist at TrackoBit. With a strong background in media and communications, she adds much-needed balance and brevity to TrackoBit’s... Read More
Related Blogs
-

5 Best Driver Behavior Monitoring Systems for 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 23, 2026Having the best driver behavior monitoring system is a necessity as it helps you ensure driver safety and optimize operational…
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.