-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is GPS and How Does GPS Work?
- Author:Anvesha Pandey
- Read Time:10 min
- Published:
- Last Update: May 27, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
Are you one of those who want to know everything about GPS technology, the past, present, and future, the ins and outs of the technology? Stop searching anymore as this piece is going to answer all your queries.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Did you know the constellations are not only made of stars but also of high-tech satellites circling Earth 24/7, just to tell you where you are? This system uses radio signals to navigate your location considering the latitude, longitude, and altitude. Well, this all happens via GPS – the Global Positioning System.
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of GPS technology and see how it transforms simple radio signals into your personal positioning system.
But before we start this long journey to know everything about GPS, here’s an interesting fact –
According to the study of g2- Currently, a GPS fleet tracking solution is being utilized by 64% of fleet managers within their organization, which marks an 8.5% rise compared to the previous year.
What is GPS? – Meaning
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system that allows users to determine their precise location considering the latitude, longitude, and altitude anywhere on the Earth.
GPS trackers or GPS tracking systems utilize the technology to determine the location of the asset or vehicle in real time.GPS tracking systems function by utilizing a network of satellites to pinpoint the precise location of a device equipped with a GPS receiver. The receiver collects signals from multiple satellites, typically at least four, to triangulate its exact position using the time it takes for the signals to reach it.
Simply put, GPS tracking devices or systems let you know the live location, and speed of your vehicle. It even helps with vehicle diagnostics, ascertaining how many stops or halts were taken throughout the assigned trip. It does more than you can imagine.
Read this to know more:- 7 Key Benefits of GPS Tracking System
From Wartime to Everyday Necessity – The History of GPS Technology
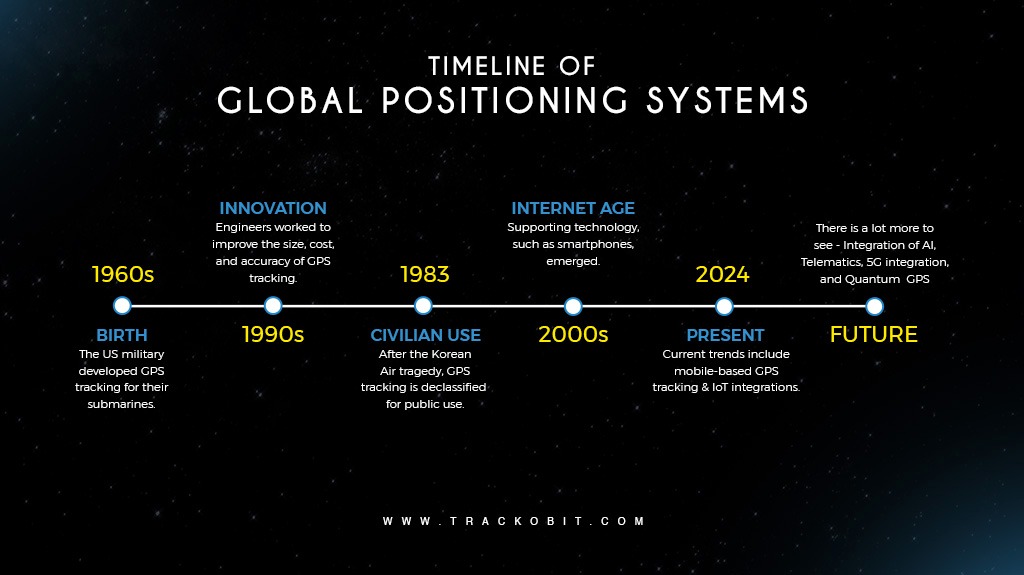
GPS technology has a long history and has evolved significantly over time. This section highlights the deep-rooted history of GPS technology (describing where it all began).
So. Let’s start – we have divided different timelines for your better understanding.
Early Concepts and Foundations (1950s – 1960s)
- The concept of satellite-based navigation was proposed during the early years of the Space Age.
- The launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union in 1957 was a pivotal moment. Scientists at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory realized that they could track Sputnik’s orbit by measuring the Doppler shift of its radio signals. This realization led to the idea of using satellites for navigation.
Launch and Deployment (1973)
- The GPS project, initially named NAVSTAR GPS, was officially launched by the U.S. Department of Defense. The system was designed to overcome the limitations of previous navigation systems by providing continuous global coverage and higher accuracy.
- The system used a constellation of 24 satellites orbiting the Earth, ensuring that at least four satellites would be visible from any point on the Earth’s surface at any time.
Full Operational Capability (1993)
- The GPS achieved Initial Operational Capability (IOC) with 24 satellites in orbit, providing continuous worldwide coverage.
- By 1995, GPS was declared to have Full Operational Capability (FOC), which means, it was fully functional and available for civilian and military use. GPS in Fleet Management (1990)
- As GPS technology became widely available, fleet management systems started incorporating GPS for real-time vehicle tracking and route planning.
- Businesses have started using GPS to monitor the location, speed, and efficiency of their vehicles, leading to improved logistics and reduced operational costs.
Modern Applications and Integration (2010 to Present)
- The integration of GPS with other technologies, such as telematics, IoT (Internet of Things), and big data analytics & even AI has revolutionized fleet management.
- Modern fleet management systems offer comprehensive solutions, including route planning, driver behavior monitoring, fuel management, and maintenance scheduling.
- Real-time data from GPS devices is used to enhance efficiency, improve safety, reduce fuel consumption, and ensure regulatory compliance.
| 📌Here’s a note- Several countries and regions have developed their own GNSS systems to compete with GPS (US) which includes GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (European Union), and NavIC (India).
The further section of this piece discusses GNSS in detail, stay tuned! |
Decoding the Signals -How GPS Guides Your Way (How Does GPS Work?
![]()
GPS systems utilize satellites to determine the exact location of a vehicle, asset, or any other valuable consignment by calculating distances using radio signals.
Like many other GNSS constellations, GPS functions on three main segments: the space segment, the control segment, and the user segment. This method is also known as Triangulation or the GPS working principle.
Let’s dig into this in detail-
Satellites in Orbit
- The GPS consists of a constellation of at least 24 satellites orbiting the Earth at an altitude of about 20,200 kilometers (12,550 miles).
- These satellites are arranged so that at least four of them are visible from any point on the Earth’s surface at any given time.
Satellite Signals
- Each GPS satellite continuously transmits a signal that includes the satellite’s location and the exact time the signal was sent.
- The signals travel at the speed of light and include precise time-stamped information.
GPS Receiver
- A GPS receiver or tracker, such as those found in smartphones, cars, or GPS devices, receives the signals from multiple satellites.
- The receiver uses the time stamps in the signals to calculate the time it takes for each signal to travel from the satellite to the receiver.
Triangulation aka GPS Working Principle
- By knowing the travel time of the signals and the speed of light, the GPS receiver can calculate the distance to each satellite.
- Using the distances from at least four satellites, the receiver can determine its exact position (latitude, longitude, and altitude) through a process called trilateration.
- If only three satellites are available, the receiver can still determine its position but not the altitude.
Display of Location
Once the GPS receiver calculates its position, it can display the location on a map, provide directions, or share the coordinates with other systems or applications.
Read Blog – How Do GPS Tracking Software Work?
Unveiling GPS Accuracy (Is GPS Accurate?)
Okay, now we know how GPS originated and how it works, but you might surely be wondering if GPS is accurate or not. Let’s explore GPS accuracy together.
To be precise, the accuracy of GPS has significantly improved over the years and is generally highly accurate, typically providing you with locational data within a few meters under optimal conditions. However, the accuracy of the technology depends on many variables, such as the number of satellites available, the urban environment, and more.
Some factors that can hinder GPS accuracy include:-
- Obstructions– Buildings, bridges, and dense tree cover can block or reflect GPS signals, causing inaccuracies in location data.
- Atmospheric Conditions- Ionospheric and tropospheric delays caused by weather conditions (e.g., storms, and atmospheric pressure changes) can affect signal propagation and accuracy.
- Urban Canyons- Tall buildings in urban areas can create “canyon effects,” blocking satellite signals and reducing the number of visible satellites, thus degrading accuracy.
- Satellite Signal Quality– Issues such as satellite clock errors or ephemeris (orbital position) inaccuracies can affect the accuracy of GPS calculations.
Beyond Maps and Navigation – Unfolding the Applications of GPS
While GPS is widely recognized for its role in everyday navigation and mapping, you’ll be amazed to know that GPS applications extend far beyond these common uses. The technology has been a prominent tool for various industries to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety.
Let’s have a look in detail and how leading fleet management systems leverage various industries.
Agriculture
In modern agriculture, GPS technology enables precision farming, which involves the use of GPS-guided equipment to optimize farm-level management. Farmers can use GPS to track the location and status of their vehicles and farm equipment. That’s not all, this ideal software also helps farmers generate reports to monitor their scheduled vehicle’s and farm asset’s performance. Moreover, farmers can track when, where, and how the equipment was used.
Modern day’s fleet management software provides you with functions like
✅Real-time vehicle and equipment visibility
✅Precise farm area calculation
✅Geofencing the forbidden areas
✅Alerts and notifications for driving events & conditions
Mining
The mining sector greatly benefits from using GPS technology, improving safety, effectiveness, and output. GPS tracks the movement of equipment and vehicles, ensuring precise navigation in vast and often hazardous mining sites. It aids in the mapping and surveying of mines, helping to plan and monitor excavation and transfer activities accurately.
Construction
In construction, GPS plays a crucial role in tracking heavy machinery, site surveying, machine control, and overall project management. It allows for precise surveying and mapping, and real-time tracking and monitoring of equipment and workers. Project managers also use GPS data to monitor the progress of construction projects in real-time.
All in all the GPS technology ensures construction projects are executed accurately, efficiently, and safely.
Features to keep in mind when opting for construction fleet management software
✅Live visibility of multiple sites and equipment
✅Data to vehicle routes and engine hours
✅Fleet vehicle maintenance & service scheduling
✅Efficient trip and route planning
Logistics
In logistics and supply chain management, GPS plays a vital role in fleet tracking, route planning, and optimally scheduling fleets. Real-time GPS tracking ensures efficient management of delivery trucks to reduce fuel consumption and transit times. It enhances visibility, allowing companies to provide accurate ETAs to clients and correspond to sudden changes.
| 📌Running a fleet in agriculture, healthcare, logistics, construction, or FMCG? TrackoN it’s all-in-one fleet management solution, becomes your partner in efficiency.
Reduce costs and boost productivity with
Focus on what matters most – growing your business. Let TrackoBit handle the fleet. Want to know more? Get in touch today! |
GPS vs. GNSS: Siblings or Distant Relatives – The Difference

While GPS and GNSS might seem like siblings due to their shared purpose of providing location and time information, they are more akin to distant relatives within the broader family of satellite navigation systems.
Still confusing, we’ll clear it up for you.
GPS (Global Positioning System) is a specific GNSS developed and maintained by the United States. It is one of several global navigation systems.
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses all satellite navigation systems globally, including GPS.
Moreover, GPS is part of the larger GNSS ecosystem, which includes multiple satellite systems providing global coverage. GNSS enhances data positioning and accuracy offering improved global navigation solutions.
Charting the Present & Future of GPS in Reference to Fleet Management
Today, fleet managers and companies have more control over their fleet vehicles than ever before. GPS tracking systems are helping logistics businesses keep tabs on fuel usage, driver speeds, idle times, driving patterns, and driver routes.
It’s easy to gather data about vehicles’ past and present trips which helps gauge driver behavior and the fleet’s efficiency. Fleet managers find it easy to plan and assign vehicles on the most efficient and economical routes. It doesn’t matter the size or the type of fleet—GPS tracking devices and advanced fleet management software systems are easy to integrate and manage.
But what’s the future of such efficient systems? Ultimately, innovations such as real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance based on GPS data, and integration with IoT devices are set to revolutionize fleet operations with more precision. Also, improvement in accuracy in the location of vehicles and assets will enable better route planning, less fuel consumption, and good driver behavior.
Moreover, advancements in AI and machine learning will further automate decision-making processes, leading to more streamlined operations and enhanced overall productivity in fleet management. As an add-on, the integration of quantum GPS and 5G integration can be seen.
Overall, GPS tracking technology and fleet management software have come a long way in the past few decades, and that progress has played a pivotal role in the fleet management industry.
Know More:-
✅What’s Currently Happening in the Fleet Management Industry?
✅Expectations From Next Generation Fleet Technology In 2025
Parting Words
To sum it all up, GPS tracking has been a powerful and indispensable tool for almost every fleet management business. After all, business companies face the danger of losing 55% of their productivity and profitability without effective GPS tracking systems.
The system provides you with accurate locational data, physical asset tracking, and route optimization. GPS tracking systems provide an array of benefits including enhancing the efficiency of the fleet, increasing productivity, better asset management, and more.
Moreover, GPS technology has significantly grown over the period and it still continues to grow in various aspects. There’s a lot more to see yet.
| 📌Tired of juggling multiple tools to manage your fleet?
Introducing TrackoBit, the all-in-one GPS tracking software that seamlessly integrates with popular devices like Teltonika FMB125 and Gosafe G1C. Gain total visibility into your fleet operations with powerful features like-
|
FAQs
-
What is a GPS system?
A GPS (Global Positioning System) is a satellite-based navigation system that provides precise location and time information anywhere on Earth. It uses a network of satellites that transmit signals to GPS receivers, which then calculate their exact position based on the distance from these satellites.
-
How to find the GPS location of a vehicle?
To find the GPS location of a vehicle, you can use a GPS tracking device installed in the vehicle. These devices transmit location data to a server, which can be accessed through a web platform or mobile app. Many modern vehicles come with built-in GPS systems that can be monitored using the vehicle manufacturer's app or service. Alternatively, you can use a smartphone with GPS capabilities to share the vehicle's location in real time.
-
How does the GPS system work?
The GPS system works by utilizing a network of satellites orbiting the Earth. These satellites continuously broadcast signals that are received by GPS receivers on the ground. The receiver calculates its distance from at least four satellites by measuring the time it takes for signals to travel from the satellite to the receiver. Using this information, along with the known positions of the satellites, the receiver can triangulate its exact location (latitude, longitude, and altitude).
-
What is the application of GPS in surveying?
GPS is extensively used in surveying for various reasons mentioned below- - Precise mapping and cartography. - Land surveying to establish boundaries and property lines. - Construction layout and site preparation. - Geodetic control and establishing reference points for spatial data.
-
What are the different types of GPS?
The primary types of GPS include- Handheld GPS- Portable devices used for outdoor activities like hiking, geocaching, and surveying. Vehicle GPS- Systems installed in cars and trucks for navigation and tracking. Smartphone GPS- Integrated into mobile phones for various applications, including maps, fitness tracking, and location services. Marine GPS- Specialized systems for navigation and tracking in maritime environments. Aviation GPS- Used in aircraft for navigation, flight planning, and safety. GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)- An umbrella term that includes GPS and other satellite systems like GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China).
-
What are the benefits of GPS?
The benefits of GPS include- Navigation- Provides accurate directions and real-time traffic updates, improving travel efficiency. Tracking- Enables the monitoring of vehicles, assets, and individuals, enhancing security and management. Safety- Helps in emergency response by providing precise location information for search and rescue operations. Efficiency- Optimizes routes and resource allocation in industries like logistics, agriculture, and construction.
-
What is GNSS technology?
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) is a term used to describe satellite navigation systems that provide global coverage. It includes not only GPS (U.S. system) but also other systems such as GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (European Union), and BeiDou (China). GNSS technology combines signals from multiple satellite constellations to improve the accuracy, reliability, and availability of positioning data.
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of GPS technology?
GPS technology offers significant advantages such as precise location tracking, global coverage, enhanced navigation, and improved efficiency in logistics and emergency response. However, it can be affected by signal blockages in urban canyons or dense foliage, and there are concerns regarding privacy and data security due to tracking capabilities.
Anvesha is a communication specialist at TrackoBit. With a strong background in media and communications, she adds much-needed balance and brevity to TrackoBit’s... Read More
Related Blogs
-

5 Best Driver Behavior Monitoring Systems for 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 23, 2026Having the best driver behavior monitoring system is a necessity as it helps you ensure driver safety and optimize operational…
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.