-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
3PL vs. 4PL: Which is Best for Your Business?
- Author:Tithi Agarwal
- Read Time:10 min
- Published:
- Last Update: June 16, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
Confused about choosing between 3PL and 4PL for your retail supply chain? Read this blog to find out which is best for your business!
Table of Contents
Toggle
Choosing the right logistics provider is crucial for every manufacturer or retailer, as this can be a make-or-break decision. As wrong decision will lead to higher logistics and warehousing costs, inefficiencies, and poor supply chain management. Ultimately resulting in dissatisfied customers.
To help you end this confusion about choosing 3PL or 4PL providers, read this article until the very end. These key differences will unlock the secret to mastering your complex supply chain!
What is 3PL or Third Party Logistics?
3PL stands for third-party logistics. It refers to companies that provide outsourced logistics services on behalf of shippers. The third-party logistics provider does not take ownership of goods but acts as an intermediary who handles transportation needs, warehousing, and other supply chain activities.
Common Services 3PLs Provider Provide:
- Multi-modal Transportation (truck, rail, ocean, air)
- Warehousing and storage management
- Inventory management
- Order processing and fulfillment
- Packaging and assembly
- Freight forwarding and customs brokerage
Without acquiring physical assets, 3PL services enable companies to use logistical knowledge, access top-notch infrastructure, and grow their logistics capabilities. This helps shippers and manufacturers free up their working capital and reallocate resources to key areas of improvement.
Retailers and e-commerce companies frequently use 3PLs for order fulfilment and shipment.
What is 4PL or Fourth Party Logistics?
4PL, or Fourth-Party Logistics, refers to a logistics model in which a company outsources the management of its entire supply chain to a fourth-party logistics provider.
The 4PL providers, also known as lead logistics providers (LLPs), typically act as supply chain integrators, overseeing and coordinating all aspects of the supply chain on behalf of the client.
This includes managing various 3PLs, carriers, and other service providers, optimizing processes, leveraging technology, and providing overall supply chain visibility and control.
Common Services 4PLs Providers Provide:
If we put it simply, 4PL services typically include:
- Strategic planning and network optimization
- Managing relationships with logistics company and multiple 3PLs
- Integrating supply chain systems and visibility
- Warehouse and transportation sourcing
- Last-mile and same-day delivery
- Freight spend management
- Compliance and risk management
- Data analytics and reporting
How Does the 3PL Process Work?
Here are the steps showing how 3PL works to provide faster delivery of goods.
1. Set up and integration
First, onboarding starts with a review of your supply chain’s particular demands and specifications. The 3PL queries such as:
How many orders and inventories do you handle? How quickly must you deliver goods to customers? Do you need any specialized services, such as labeling or kitting?
After that, the 3PL sets up procedures for interfacing with ERPs, OMSs, and other technological platforms. Data interchange and API interfaces make order handoff and status updates easy.
2. Transportation management
Once the setup is complete, the 3PL transportation process arranges outbound shipping from suppliers and the manufacturing facility to the 3PL warehouse.
Proper route planning and carrier pairing optimize transit routes, modes, and costs.
3. Warehousing and inventory management
At the warehouse, the 3PL receives and checks in supplier shipments. Inventory is stored, tracked, and replenished accurately.
4. Order fulfillment
The 3PL selects, packs, and ships orders from customers’ inventories. Orders are labeled for shipping, verified for accuracy, and safeguarded using robust packing materials.
5. Delivery
The 3PL bids goods to the selected carriers for ultimate client delivery. During transit, updates on the location and status are shared with all stakeholders. Delivery options for business clients could include inside delivery, tailgate service, or white glove service.
6. Returns and reverse logistics
And we can’t forget about returns!
Many 3PLs are also capable of handling reverse logistics and returns. They handle damaged and extra inventory, inspect and accept returned goods, and interact with customers regarding processing refunds..
This entire procedure demonstrates how 3PLs manage all the intricate paperwork associated with operational logistics. They make it appear effortless, freeing you up to concentrate on your main business!
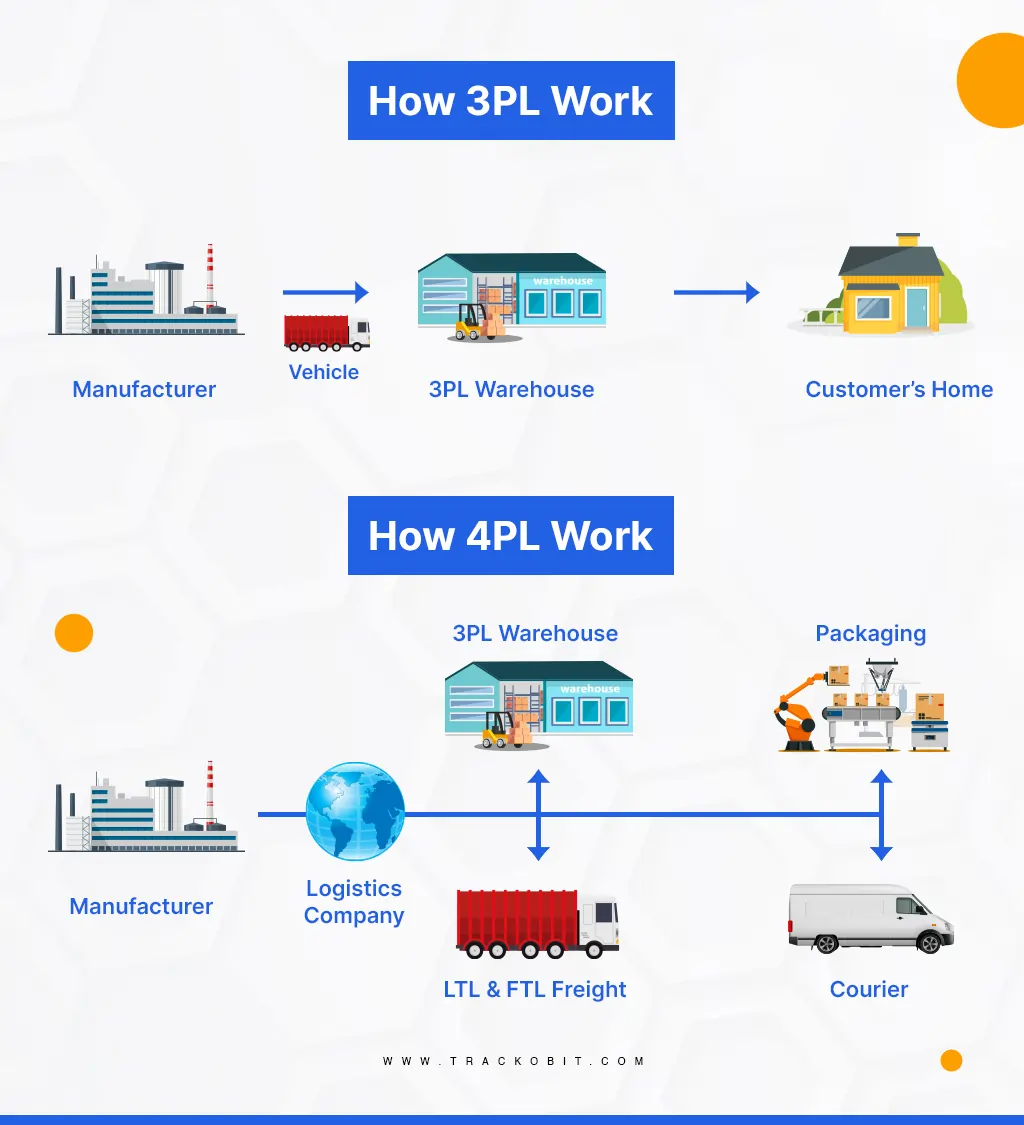
Stages of 3PL & 4PL
How the 4PL Process Works?
If a company opts for a 4PL to manage and optimize its supply chain, and logistics process, the providers help even in strategizing and consulting by:
1. Extensive analytics and strategic planning
The client’s supply chain activities are first thoroughly examined by the 4PL provider. The logistics suppliers know the client’s objectives, difficulties, and particular needs.
The 4PL then creates a strategy plan in accordance with the assessment. The plan describes the best technology, logistics procedures, and supply chain organisation to achieve the client’s goals.
The plan even entails identifying the top carriers and third-party logistics providers to carry out tactical operations effectively.
2. Supply chain network design and optimisation
The 4PL designs the overall structure of the supply chain network. It includes the number and location of distribution centers, transportation routes, and inventory placement. To enhance efficiency with route optimization software.
3. System integration for visibility
To obtain end-to-end visibility, the 4PL continuously integrates systems throughout the logistics network.
The 4PL integrates cutting-edge technology to provide and gain insight across the whole supply chain. This technology provides data analytics, inventory management systems, and real-time tracking.
4. Coordination and collaboration
The 4PL connects the client and various stakeholders. It arranges for the cooperation of manufacturers, carriers, suppliers, and other outside logistics companies.
Coordination and communication between all stakeholders are guaranteed by effective collaboration. Like sharing delivery information and ETA of consignment and parcels with customers.
5. Monitoring KPIs
The 4PL closely monitors Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) throughout the operations to spot inefficiencies and potential areas for improvement.
Their supervision guarantees that the supply chain achieves its goals while also improving compliance and reducing risks.
6. Strategic recommendation for improvement
The 4PL provides innovative ideas and strategic recommendations to continuously improve the supply chain at the end of the operational cycle.
Their suggestions provide long-term benefits and modifications to match changing business requirements.
Although not directly involved in daily operations, the 4PL offers supervision that directs strategic optimisation at every stage.
The client can concentrate on their main business with this strategy while the 4PL handles the complex supply chain management.
What are the Advanatages and Disadvanatages of 3PL
Advantages
- Specialized expertise: 3PLs are experts in particular logistics tasks; they offer specialized knowledge in distribution, warehousing, and transportation.
- Cost efficiency: Companies that lack internal knowledge might save money by contracting with third-party logistics suppliers to handle specialized logistics activities.
- Scalability: 3PL services are often scalable, allowing businesses to adjust logistics support according to fluctuations in demand.
- Focus on core competencies: By outsourcing logistics activities to a 3PL, businesses can concentrate on their core competencies and strategic priorities.

Advantages of Third-party Logistics
Disadvantages
- Limited scope: 3PLs provide specific logistics services without a comprehensive view of the customer’s supply chain.
- Dependency on multiple partners: Businesses using multiple logistics providers may face challenges in coordination and communication, leading to potential inefficiencies.
- Less strategic oversight: A 3PL’s focus is on operational execution, and it may not provide strategic oversight or long-term supply chain optimization.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 4PL
Advantages
- End-to-end supply chain optimization: 4PLs provide an all-encompassing perspective of the supply chain, streamlining every process step for increased effectiveness.
- Strategic partnership: 4PLs participate in strategic alliances, offering advisory opinions and suggestions to match company objectives with the supply chain.
- Single point of contact: When businesses work with a 4PL, they have a single point of contact for managing and arranging different logistics tasks and service providers.
- Advanced technology integration: 4PLs use cutting-edge technology to provide real-time analytics, visibility, and decision-making throughout the supply chain.
Advantage of Fourth-party Logistics
Disadvantages
- Complex implementation: Implementing a 4PL model can be complex and may require significant organizational changes to integrate the supply chain fully.
- Potential for overreliance: There’s a risk of overreliance on a single entity (the 4PL), which could pose challenges if issues arise or if the 4PL fails to meet expectations.
- Higher costs: 4PL services, with their comprehensive scope and strategic focus, may be more expensive than specific 3PL services.
What are the Key Differences Between 3PL and 4PL?
Understanding the key difference between 3PL and 4PL enables smarter supply chain decisions.
1. Scope of services and specialisation
Transportation, warehousing, and distribution are examples of integrated supply chain services commonly offered by 3PLs. These services center on how supply chain operations are carried out.
A 4PL assumes a more involved position. It manages and optimizes the complete supply chain, including planning, coordination, risk management, and continuous improvement, while outsourcing execution. It performs supply chain integration duties and specialized tasks like packaging, labeling, contracting logistics providers, etc.
2. Asset ownership
Warehouses, distribution hubs, vehicle fleets, and inventory are examples of the physical logistics resources that 3PLs sometimes own or lease. This gives them direct control over the execution of operational tasks.
4PLs do not own logistics assets. Instead, they oversee and manage networks of outside carriers, 3PLs, and other logistics service providers. Rather than relying on tangible assets like warehouses, 4PLs use technology and strategic alliances.
3. Strategy and execution
3PLs focus on the day-to-day execution and management of logistics, including product transportation, warehouse operations, and shipping orders. They offer the necessary infrastructure for carrying out these tactical tasks.
4PLs manage the company’s logistics operations and build ideal supply chain networks at a strategic, consultative level. 4PLs oversee, coordinate, integrate, optimize, and analyze activities throughout supply chains.
4. Technology
3PLs use technology such as EDI, warehouse management systems, transportation management systems, and others to carry out operational logistics tasks.
4PLs implement advanced integration, optimization, predictive analytics, and end-to-end visibility tools. To help with supply chain strategic decision-making and offer insights.
5. Customer interaction
3PLs usually deal directly with the client, concentrating on the logistics tasks they are contracted to complete. They are task-oriented and center around their logistical services, including distribution, warehousing, and transportation.
A 4PL’s customer communications are more comprehensive and include the whole supply chain. This entails aligning the supply chain with the client’s business objectives, coordinating various logistics management tasks, and strategic planning.
6. Pricing
In 3PL agreements, pricing is frequently transactional or dependent on certain parameters, including the quantity of products transported or kept. Within the agreement’s parameters, clients pay for the services they consume.
In 4PL contracts, pricing may be determined by combining fixed fees with incentives depending on performance. The pricing structure reflects the complete nature of the services offered, which encompass both strategic and operational aspects.
7. Flexibility
Within the parameters of their assigned logistical roles, 3PLs provide flexibility. Based on their needs, clients can select particular services and scale them up or down in response to changes in customer demand.
4PLs offer strategic flexibility. They modify the whole supply chain plan in response to market shifts, corporate goals, or other outside variables.
8. Control over operation
Clients maintain overall control over their supply chain strategy, while 3PLs offer operational management within the parameters of their designated responsibilities. The 3PL adjusts to the client’s needs while remaining within the contract’s parameters.
The 4PL oversees and coordinates a variety of logistical tasks, giving it more authority over the whole supply chain. Customers gain from a more detached attitude as the 4PL becomes more involved in optimization and decision-making.
How TrackoMile Enhances 3PL and 4PL Solutions?
Be it 3PL or 4PL, both can benefit from using TrackoMile’s last-mile delivery software. It has solutions that will enhance the functionality of the logistics process. It is useful in the final stages, where its integration can help accelerate the delivery of orders from distribution centres to customers’ homes.
Dynamic Dispatch
With its dynamic dispatch management feature, TrackoMile optimizes the process of pairing orders with riders. It automates the process after considering multiple factors such as:
- Nature of the order
- Priority of the order
- Delivery time window
- Availability of the rider
And more.
Load Management
This feature is essential for optimizing payload capacity. It pairs orders with the right vehicles so that more orders can be delivered with fewer vehicles. It pairs after considering factors such as:
- Type of Order
- Size, width, and dimension of orders
- Distance from warehouse to customer’s
- Availability of vehicles
Route Optimization
Route optimization solution helps 3PL and 4PL services deliver orders on-time by suggesting the shortest and most efficient routes. It auto sequences the stops optimally so that the last mile delivery operation is fuel, cost, and time efficient. It does it by optimally factoring 120+ factors, like
- Road conditions
- Traffic conditions
- Weather conditions
- Vehicle type
And more.
Performance Reports
These real-time reports are a big help to logistics providers, be it 3PL or 4PL. They provide accurate information on the success of the delivery operation and show various analytics regarding the delivery and the entire process.
Real time Tracking
TrackoMile is renowned for its accuracy and real-time tracking capabilities. It automates the process of tracking riders and parcels. It shares ETA with all stakeholders, be it dispatchers or customers. Keeping everyone informed.
The best part of TrackoMile is that it can easily be integrated with other software that third-party logistics or fourth-party logistics providers might be using. Such as inventory management or warehouse management software to ensure goods move smoothly throughout the supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the types of logistics services?
Here are the 5 types of logistics service providers: 1. A 1PL (first-party logistics) provider transports goods and products directly from one location to another. 2. A 2PL (second-party logistics) provider owns the transportation means while distributing products for their customer. 3. A 3PL (third-party logistics) provider manages all aspects of fulfillment, from warehousing to shipping. 4. A 4PL (fourth-party logistics) provider manages a 3PL for the customer and other aspects of the supply chain. 5. A 5PL (fifth-party logistics) provider, also known as a ‘logistics aggregator,’ manages a business's entire supply chain network.
-
What types of businesses are best suited for a 3PL model?
The types of businesses that are best suited for the 3PL model are small to medium-sized businesses with specific logistics needs, limited resources, and a focus on tactical operations.
-
Is 4PL better than 3PL?
Whether 4PL is better than 3PL depends on your business needs. For enterprise-level businesses with more complex logistics processes, 4PL may be more appropriate.
Tithi Agarwal is an established content marketing specialist with years of experience in Telematics and the SaaS domain. With a strong background in literature and industrial expertise in technical wr... Read More
Related Blogs
-

12 Must-Have Features in Last Mile Delivery Solutions
Mudit Chhikara March 13, 202612 essential features every last mile delivery solution must have to ensure faster deliveries, lower costs and better customer experience.
-

14 Best Practices for Last Mile Delivery Optimization (2026)
Tithi Agarwal March 13, 2026Last-mile delivery optimization is an absolute necessity in 2026. Learn how methods like route optimization, ePOD and 12 other proven…
-

B2B Last-Mile Delivery: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategy, Challenges & Optimization
Parul Choudhary March 9, 2026B2B last-mile delivery requires careful planning and clear visibility. This guide covers strategy, challenges, and optimization methods to boost delivery…
-

What is Proof of Delivery (POD)? A Complete Guide for Modern Logistics in 2026
Shemanti Ghosh February 26, 2026In modern logistics, proof of delivery (POD) confirms that a shipment has been delivered using OTP, photos, or e-signatures. This…

Subscribe for weekly tips to supercharge your last-mile delivery.
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.