-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is Reverse Logistics?
- Author:Tithi Agarwal
- Read Time:5 min
- Published:
- Last Update: September 2, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
Reverse logistics is an integral part of supply chain management and holds the power to help companies retain their consumers and provide insights into their purchasing habits.
Table of Contents
Toggle
The customer is king for any brand or retailer, and making reverse logistics smooth is a dire requirement. Reverse logistics is vital for supply chain management as it maintains the flow of goods, reduces cost and, most importantly, helps retain customers.
In the past few years, the global logistics industry has witnessed an increase in parcel returns, recovery, exchange and redistribution. Around 25 to 30 percent of e-retail orders are often returned.
This article will offer insights into making reverse logistics as smooth as possible and what the future holds!
What is Reverse Logistics?
Walmart processes 45 million cases of returned merchandise.
Reverse logistics is a supply chain management type comprising of goods moving from the customers back to the sellers or manufacturers. Here, the end customer changes. Instead of the consumer, it’s the manufacturer or supplier. Once the end consumer receives the product, it can be processed as a return or recycled.
The end consumer, aka manufacturers, is responsible for the final product disposal in the form of recycling, refurbishing or resale. Companies have to resort to reverse logistics when customers raise return or exchange tickets.
Worldwide, returns are worth almost a trillion dollars annually and have become increasingly common with the growth of e-commerce.
Smooth reverse logistics aims to regain value and ensure repeated customers. Companies leverage reverse logistics to build customer loyalty, repeat business, and minimise returns-related losses.
How Reverse Logistics Works?
Reverse logistics involves moving the goods backwards from the traditional end of the supply chain to sellers. The process needs to be as neat and smooth as possible. Many companies prefer to outsource this process to 3PL.
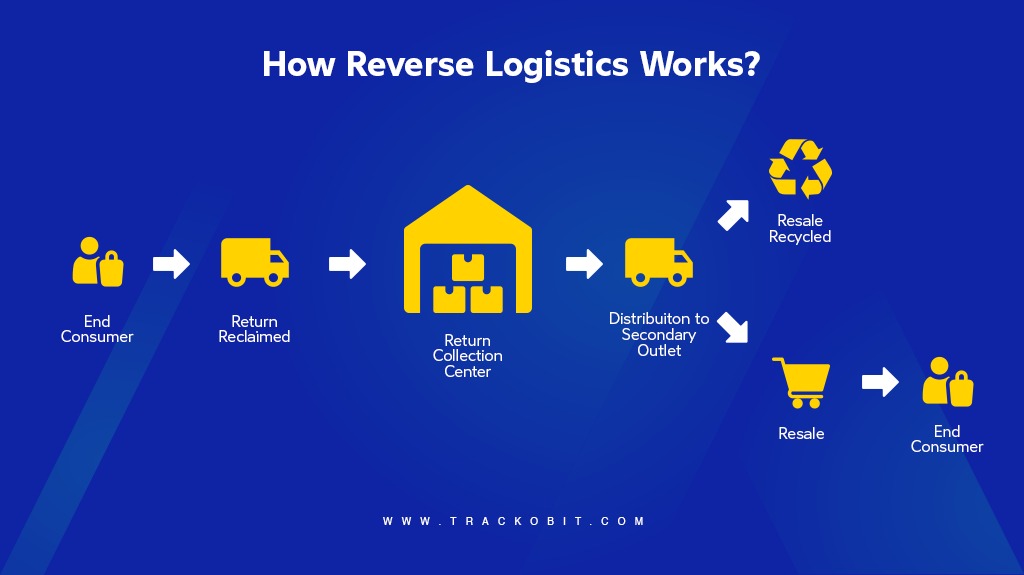
Steps to Good Reverse Logistics
Process the Returns: The very first step to reverse logistics begins with consumers raising a ticket for returning a product. This step entails return authorisation and identifying product conditions. This part also involves scheduling return shipments, approving refunds and exchanging faulty products.
Deal with Returns: Once the returned product reaches the centralised processing unit, inspection determines its return category –
- Fix
- resell as new,
- resell as return
- recycle,
- scrap or refurbish.
Keep Returns Moving: Sellers will reduce daily wastage by sending repairable products to the repair department.
Repair: After thoroughly reviewing the items, it is determined whether the products will be repaired or fit for selling as sellable parts.
Recycle: Any part of the product that is beyond repair or reselling will be sent for recycling.
Reverse Logistics vs Traditional Logistics
Here’s a table outlining the key differences between traditional logistics and reverse logistics:
| Factors | Traditional Logistics | Reverse Logistics |
| Definition | The process of moving products from the manufacturer to the consumer, typically in a forward direction. | The process of moving products from the consumer or end user back to the manufacturer or a designated location for recycling, remanufacturing, or disposal. |
| Flow Direction | Forward, from manufacturer to consumer. | Reverse, from consumer to manufacturer or designated facility. |
| Objective | Efficiently deliver products to meet customer demand. | Manage returns, recycling, and disposal of products, often with an emphasis on environmental sustainability. |
| Focus | Emphasis on order fulfilment, transportation, and inventory management. | Emphasis on returns management, recycling, refurbishing, and waste reduction. |
| Typical Activities | Warehousing, transportation, order processing, and inventory management. | Returns processing, recycling, remanufacturing, waste management, and disposition of returned goods. |
| Key Challenges | Inventory control, demand forecasting, and minimising transportation costs. | Managing returns, disposition of unsellable goods, recycling, and regulatory compliance. |
| Customer Involvement | Mostly a one-way process with minimal customer involvement. | Involves customer returns, which require communication and coordination with customers. |
| Environmental Impact | Mainly focused on product delivery and may not consider environmental concerns. | Focused on sustainable practices, recycling, and minimizing waste, making it more environmentally conscious. |
| Cost Consideration | Costs related to transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. | Costs related to returns processing, recycling, waste disposal, and compliance with regulations. |
Why is Smooth Reverse Logistics Gaining Traction?
Reverse logistics holds much more importance than we know, as it maintains an efficient flow of goods in the supply chain. The process reduces costs, creates value, decreases risk and completes the product cycle.
Benefits of Reverse Logistics:
Provide Valuable Product Data
One of the major benefits of an effective reverse logistics process is that it provides organisations with valuable product data. This is vital as manufacturers can identify and correct the issue causing the return of the items.
Well-planned and executed reverse logistics can collect data and the correct reason behind returns and exchanges.

Reduced Losses and Additional Revenue
Proper, automated and streamlined management of goods and materials travelling back up the supply chain can result in reduced losses and additional revenue.
For example, flexible return policies and error-free returns handling can save on returns-related losses. Compounding this is the fact that proper handling and distribution of returned goods can result in additional sources of revenue and reduced losses.
This additional revenue can be realised by refurbishing, repairing, and recycling goods or selling returned products or materials.
Enhanced Service
A high-functioning reverse logistics department and its processes will offer superior service to disappointed customers upon returning their items.
In competitive markets, enhanced services in the form of return processing is a critical point in brand/customer relationships. Social media sharing and customer influence online can have very material impacts on a company’s reputation and footing in the market.
Good Brand Image
Considering that an improved reverse logistics process yields heightened service levels and acts to reduce negative publicity, it will naturally result in enhanced levels of brand image. Brands offering recycling for end-of-life goods enjoy recognition for efficiency and good practices.
| Apple’s reverse logistics process offers customers discounts when purchasing a new Apple product in exchange for an old one. Not only is this policy helping Apple reap positive publicity, but it is also financially beneficial. As Apple is reusing parts and materials from the end of life products.
H&M is using reverse logistics in a very innovative manner. It is accepting gently used clothing from any brand, not only the H&M brand. It is from these previously owned garments that they make their entirely recycled apparel line. This policy is helping H&M keep the customers engaged with the brand by selling them clothes and making them feel like important contributors to a greener future. |
Customer Retention
Another precious benefit of effective reverse logistics is increased customer retention. As mentioned above, easy returns and safe handling are pivotal points in the customer/brand relationship.
According to a published research, 95% of consumers surveyed stated they would not buy from a brand again if they undergo a negative return experience.
Ensuring the customer is handled well and returns are picked up timely and conveniently can substantially increase customer retention.
Challenges of Reverse Logistics
Increased Complexity
Reverse logistics adds complexity to the supply chain due to the need to track and manage returned products. Because there are so many uncertainties in returns and reverse logistics, it’s difficult for manufacturers to keep track of orders and manage information flow.
Businesses are readily adopting systems that provide end-to-end visibility and control in such an environment.
Higher Shipping Costs
Shipping costs are often higher for reverse logistics as the products must be returned to the suppliers.
As a consequence of rising return volumes, corporations are having difficulty determining the extent of product failures or damage and incurring additional expenses for repackaging and redistribution.
The Ecological Issue
Reverse logistics is closely associated with environmental protection since it is responsible for handling the goods, components, and materials that have been used or disposed of and for which the producer is liable in some manner.
How to Put into Action Efficient and Successful Reverse Logistics?
The answer is automation of the process with the help of last mile delivery software such as TrackoMile. By adopting the software, the companies will mitigate all challenges and embrace the benefits of smooth reverse logistics.
Route Optimisation: the software suggests the most optimised routes after considering 120+ factors. All you have to do is feed in the addresses and watch as the software does most of the work.
Carrier Management: Pickup for sofas; confused about which vehicle to assign. Carrier management solution helps you by automatically pairing the best-suited vehicle for reverse logistics by considering 50+ factors.
Rider Roster: The roster displays the number of riders and carriers at the shift and day for smoother reverse logistics. Making it easy to schedule pickups.
Scheduled Pickups: Companies no longer have to worry about second-attempt pickups and related costs. Scheduled pickups are possible with the help of route optimisations and dynamic dispatch management.
Rider Application: Complete optimisation of reverse logistics with the rider app, which allows them to mark their attendance remotely, accept orders and pickup requests, scan barcodes and OTP. They get complete information on the product pickup, their trips, and stops.
PODs: TrackoMile supports multiple PODs, such as OTP, eSignatures, barcode scanning, and automatic authentication. Riders can collect them on their rider app.
The Future of Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics is an integral part of the supply chain and is expected to grow in importance. Companies that manage returns and recalls effectively will be well-positioned to succeed in the ever-changing retail landscape.
The future of reverse logistics is uncertain, but several trends could impact the industry. These include:
Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility: With increasing environmental concern, reverse logistics will continue to prioritise sustainability. This means a greater focus on recycling, refurbishing, and reducing waste. Companies will adopt eco-friendly practices and find innovative ways to repurpose returned products or components.
Technology and Data Analytics: Integrating technology, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, blockchain, and data analytics, will enhance the visibility and tracking of returned items. Real-time data will provide insights into product condition, location, and disposition, leading to more efficient handling and decision-making.
Automation and Robotics: Automation, including robotics and AI-driven solutions, will play a significant role in reverse logistics. Automated systems can sort, process, and refurbish returned items more efficiently, reducing labour costs and errors.
Consumer-Centric Solutions: Customer expectations for hassle-free returns and exchanges will drive innovation in reverse logistics. Companies will offer convenient and transparent return processes to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Reverse Logistics Service Providers: Specialized reverse logistics service providers will emerge, offering expertise in managing the complexities of handling returned products, recycling, and compliance with regulations.
Power Up your Reverse Logistics
It’s the responsibility of companies to strategise and optimise their reverse logistics. The reason is that they are accountable and responsible for the disposal of the products and their environmental impact while also ensuring the convenience of the customers.
TrackoMile is more than capable of helping businesses ensure the smooth return of the products that will involve the scheduling and picking process. As last mile delivery software offering automated solutions that help cater to top customer expectations.
Tithi Agarwal is an established content marketing specialist with years of experience in Telematics and the SaaS domain. With a strong background in literature and industrial expertise in technical wr... Read More
Related Blogs
-

What is Proof of Delivery (POD)? A Complete Guide for Modern Logistics in 2026
Shemanti Ghosh February 26, 2026In modern logistics, proof of delivery (POD) confirms that a shipment has been delivered using OTP, photos, or e-signatures. This…
-

Top 9 Delivery Management Software in 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 2, 2026By choosing the best delivery management software, companies can benefit from features like route optimization, dispatch management, and more. This…
-

How Rider Tracking Software Improves Delivery Accuracy and Reduces Fraud
Tithi Agarwal December 8, 2025Rider tracking software improves delivery accuracy with real-time GPS visibility and automated ePOD. It also enables route optimisation and fraud…
-
Top Electronic Proof of Delivery (ePOD) Software in 2026
Tithi Agarwal September 25, 2025Electronic proof of delivery has become the backbone of modern logistics. Explore the top 8 ePOD software in 2026 and…

Subscribe for weekly tips to supercharge your last-mile delivery.
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.