-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is an Electronic Logging Device (ELD): Benefits, Working & Compliance
- Author:Tithi Agarwal
- Read Time:8 min
- Published:
- Last Update: December 2, 2024
Table of Contents
Toggle
Learn how electronic logging devices (ELD) can help prevent driver fatigue and ensure compliance with HOS regulations. It is time we focus on driver safety.
Table of Contents
TogglePart of fleet managers’ duties is maintaining error-free logbooks of their vehicles’ HOS. However, by pairing electronic logging devices (ELDs) with fleet management software, this mountainous task can be conquered.
Have you heard of this technological advancement yet? If not, you might be missing out on all its benefits.
To help you catch up, here is a concise guide to ELD benefits, working, history, and compliance. Get reading!
🔊 What are Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs)?An electronic logging device (ELD) is a piece of electronic hardware. Owners attach it to commercial motor vehicles. It automatically records a driver’s hours of service (HOS) and other relevant data. ELDs synchronize with the vehicle’s engine to track driving time and engine hours. It also monitors vehicle movements and collects locational information. These devices also have GPS trackers, which help to replace traditional paper logbooks. Regulative authorities in many jurisdictions mandate them. This ensures compliance with HOS regulations, promotes road safety, and prevents driver fatigue. |
Now that you know the meaning, let us know how the journey of ELD started.
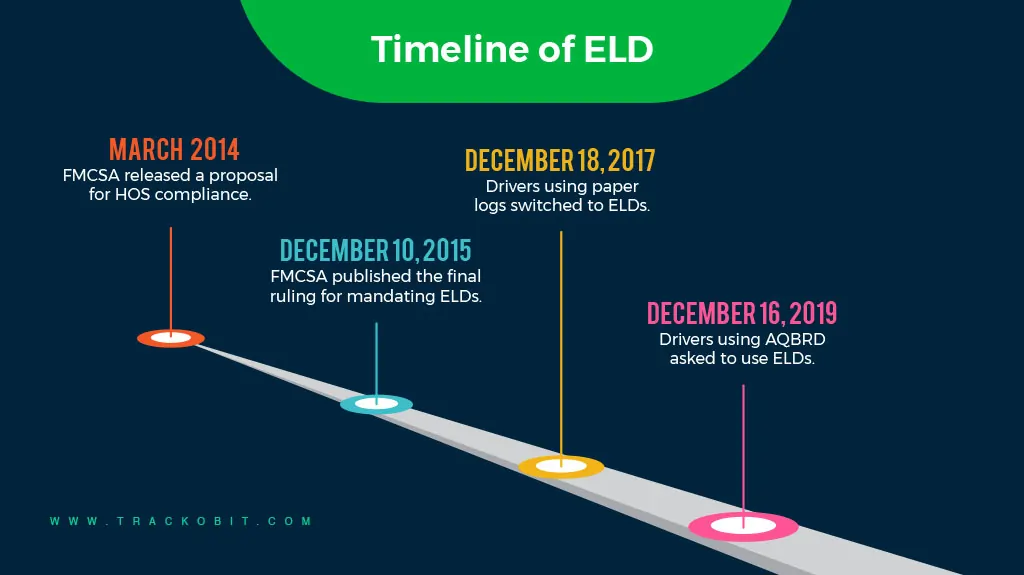
Timeline of ELD Mandate: History & Important Dates
Timeline of ELD
The FMCSA implemented a timeline for ELD compliance. This approach was designed to provide sufficient time for awareness and transition.
✅In March 2014, The FMCSA issued a notice of proposed rulemaking. It outlined amendments to safety regulations to establish the ELD mandate. Comments regarding the proposed rulemaking were required to be submitted by May 2014.
✅On December 10, 2015, the FMCSA published the final ruling for the ELD mandate.
✅ On December 18, 201, drivers using paper logs were asked to switch to ELDs.
✅ By December 16, 2019, full compliance was required in adherence to the FMCSA guidelines. Any drivers or carriers still using AOBRDs had to transition to ELDs on this date.
How Does an Electronic Logging Device Work?
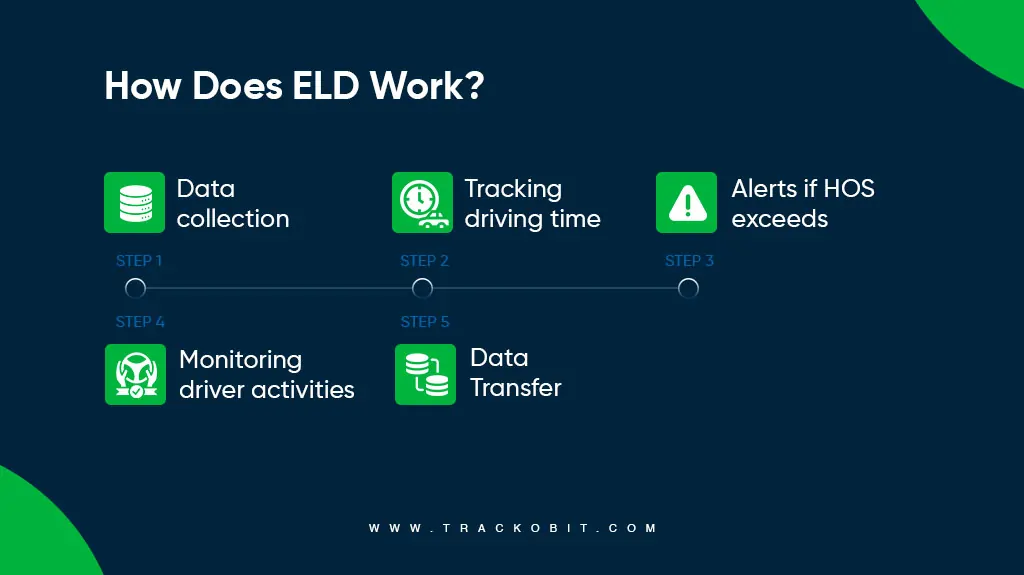
It is important to know how this ELD works. Here are the steps detailing how:
Step 1 – ELD Installation and Data Collection
The devices are installed into vehicles by plugging into the commercial vehicles’ OBD port. From here, it pulls data directly from the engine. This data includes whether the engine is on/off. Data on the amount of fuel consumed and distance traveled is obtained.
Also, drivers use the driver app to log HOS. Additionally, ELDs have built-in GPS trackers. These are useful in collecting data on vehicles’ precise location.
Step 2 – Driving Time Tracking
One of the prime uses of trucking ELDs is tracking driving time. The device automatically records the start and end of each driving session. It also tracks/records any breaks or rest periods taken by drivers.
Working of ELD devices
Step 3 – HOS Compliance
Commercial vehicle electronic logging devices record Hours of Service. Compliance with this regulation, as set by the Department of Transportation, is essential. According to this regulation, drivers can operate for a fixed duration. After that, taking breaks is mandatory.
Step 4 – Real-time Monitoring
After receiving engine hours data, it becomes necessary to monitor driver behavior. This HOS tracking device provides real-time monitoring of driver activity.
This is beneficial as now managers have clear info on their fleet’s location and status. This is a must for improving the safety of the drivers, vehicles, and consignments.
Step 5 – Data Transfer
After collecting and processing, all the important yet raw data is transmitted to authorities like managers and the government. For example, this data is used throughout the different levels of DOT inspection. Fleet management software even uses the data to improve driver behavior.
ELD devices transmit data through cellular services, Bluetooth, or Wifi (usually inbuilt).
Who Needs an Electronic Logging Device?
The requirement is not limited to short or long-haul logistics companies. If an individual has at least eight hours of duty status logins within 30 days, they will require an ELD.
Here are those who fall under the mandate:
- CMV drivers are mandated to use ELDSs. This includes drivers operating vehicles that weigh more than 10,000 pounds. Also, if transporting hazardous materials or more than eight passengers.
- CMV drivers who engage in interstate commerce. This involves transporting goods or passengers across state lines.
The FMCSA does allow ELD-exempt status for drivers who are not required to keep Record of Duty Status (RODS), as well as
- Drivers who utilize RODS for a maximum of eight days within a 30-day timeframe.
- Drivers operating vehicles manufactured before the year 2000.
What are the Benefits of ELDs?
These automated logging devices help with the digital logging of drivers’ hours of service. The device ensures optimum hours of service. This is essential for checking driver fatigue and increasing their safety on the road.
Let’s look into some of the major benefits served by electronic logging devices.
1) Improved Compliance
Electronic logging devices help ensure compliance with Hours of Service regulations by accurately recording a driver’s driving time and rest periods. This reduces the likelihood of violations and the penalties associated with them.
2) Accurate Record Keeping
ELDs automatically track driving time, which further helps eliminate the need for manual paper logs. This reduces the chances of human error and inaccuracies related to record keeping. This further helps in ensuring more precise data for regulatory compliance and billing purposes.
3) Enhances Safety
By promoting adherence to HOS regulations, ELDs contribute to safer driving practices by reducing instances of driver fatigue and drowsiness. This, in turn, helps lower the risk of accidents caused by tired drivers.
4) Streamlined Operations
Electronic logging devices (ELDs) provide real-time access to driving data, allowing fleet managers to monitor driver activity and plan routes more efficiently. This can lead to improved fleet management and better utilization of resources.
5) Data Insights
ELDs collect valuable data on driver behavior, vehicle performance, and route efficiency. Analyzing such data can help identify areas for improvement, optimize operations, and enhance overall fleet performance.
What are the Compliances Related to ELDs?
Each region has its own regulations governing Electronic Logging Device (ELD) and Hours of Service (HOS) compliance. Let’s examine ELD compliance in some countries.
1) United States
- The FMCSA mandates using ELDs for most CMVs involved in interstate commerce required to maintain RODS.
- In addition, all ELDs must comply with the technical specifications outlined in the FMCSA’s regulations. This includes features such as automatic recording of driving time, location tracking, tamper resistance, and data transfer capabilities.
- Regulations also govern HOS limits and rest periods for drivers.
2) Canada
- The Canadian Council of Motor Transport Administrators (CCMTA) mandates the use of ELDs in Canada.
- According to CCMTA regulations, electronic logging devices should comply with its technical standards. These compliances closely align with the ELD requirements of the FMCSA in the United States.
- Canadian regulations also govern HOS limits and rest periods for drivers.
3) European Union (EU)
- The EU regulates driving hours and rest periods for commercial drivers, as outlined in the EU Driver’s Hours Regulations.
- While the EU does not specifically mandate the use of electronic logging devices, digital tachographs are required to track drivers’ hours and activities.
- Digital tachographs are similar to ELDs, recording driving time, rest periods, and other relevant data electronically.
4) Australia
- In Australia, the National Heavy Vehicle Regulator (NHVR) regulates fatigue management and compliance for heavy vehicle operators.
- Electronic work diaries (EWDs) are becoming increasingly common for tracking drivers’ work and rest hours.
- EWDs must comply with technical standards established by NHVR, ensuring accuracy, tamper resistance, and data security.
5) Brazil
- Brazil’s National Traffic Council (CONTRAN) has regulations governing the use of digital tachographs in commercial vehicles.
- These devices record driving time, rest periods, and other relevant data in compliance with Brazilian HOS regulations.
- Digital tachographs must comply with technical specifications outlined by CONTRAN.

The specific requirements and terminology may vary between regions. But still, the common goal of these regulations is to promote safety and prevent driver fatigue. Also, electronic logging and monitoring systems ensure compliance with driving hour limits.
| 🔎 Name of Countries | Regulatory bodies responsible for making ELD rules |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electronic Logging Devices
Advantages of Electronic Logging Devices:
-
Accuracy
Electronic logging device accurately record driving time, reducing errors associated with manual manuals.
-
Compliance
ELDs help ensure compliance with hourly service regulations set by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) and other regulatory agencies, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
-
Efficiency
ELDs automate the logging process, save drivers and administrative staff time, and eliminate the need to manually enter data and paperwork.
-
Real-time monitoring
Some ELDs offer real-time monitoring capabilities, allowing fleet managers to track driver activity and meet safety and compliance standards.
-
Improved safety
By controlling driving hours and enforcing rest periods, ELDs help promote safer driving and help reduce the risk of fatigue-related accidents.
Disadvantages of Electronic Logging Devices:
-
High Initial Cost
The initial investment in ELD software and hardware can be high for smaller trucking companies or independent drivers. Although the prices vary from place to place, the minimum can be between $20 and $25 per month.
-
Technical issues
Like any electronic device, ELDs can have technical issues, such as connectivity issues or software errors, that can block access.
-
Learning Outcomes
Transitioning from paper record books to ELDs may require training for drivers and administrative staff, and some drivers may resist this transition.
-
Dependence on technology
Drivers who rely solely on electronic logging equipment are more susceptible to damage caused by power outages, faulty equipment, or cyberattacks.
Final Words
Electronic logging devices have actually changed the game for fleet management. These devices record compliance with HOS regulations. This is a much-needed step to improving driver safety and how CMV operations are carried out. The future surely looks exciting and safe!
This technological advancement has elevated fleet operation monitoring. When talking of fleet management, how can we not mention the OG—TrackoBit’s fleet management software?
With 99.98% accurate real-time tracking, it effortlessly enables companies to monitor multiple aspects of fleet operations.
Beyond tracking, it also helps optimize performance through a driver behavior monitoring solution. Fleet managers get alerts whenever a driver drives harshly or exceeds the speed limit. This is essential for improving driver and vehicle safety.
FAQs
-
What are the key features of electronic logging device?
Key features of ELDs include automatic recording of driving time, engine hours, and location tracking. The device also monitors real-time driver activity and ensures compliance with HOS regulations.
-
What information does an ELD record?
The electronic logging device automatically records the following data to keep records of duty status: - Date - Time - Location - Engine hours - Vehicle miles - Driver identification
-
How much do ELDs cost?
The cost of ELDs can range from hundreds of dollars to thousands per vehicle. There are several costs involved: the device hardware, a professional installation, and a monthly software fee.
-
Is an electronic logging device a GPS tracker?
Yes, the device uses GPS technology to record location data. However, the primary job is to record and monitor the driver’s HOS.
-
Can drivers edit an ELD log?
Yes, drivers can edit the log. But only if there is a mistake or information is missing. A driver or someone authorized at the carrier office can edit the record.
Tithi Agarwal is an established content marketing specialist with years of experience in Telematics and the SaaS domain. With a strong background in literature and industrial expertise in technical wr... Read More
Related Blogs
-

5 Best Driver Behavior Monitoring Systems for 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 23, 2026Having the best driver behavior monitoring system is a necessity as it helps you ensure driver safety and optimize operational…
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.