-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is a Digital Tachograph? History, How to Use It & Alternatives
- Author:Anvesha Pandey
- Read Time:8 min
- Published:
- Last Update: May 7, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
Read a lot of pieces around digital tachographs? Still not clear with what exactly is this? This piece is for you as it unfolds everything about tachographs.
Table of Contents
Toggle
It was the year 1902 when Max Maria von Weber invented the first-ever tachograph. The prime goal back then was to help railway companies document related irregularities like speed violations, irregular working hours, time adherence, and more. These challenges were the core reasons for the birth of tachographs.
Over the years, tachograph technology has evolved significantly. Digital tachographs have replaced analog ones and offer several advantages, including improved accuracy, reliability, and ease of use.
Wondering how tachographs come into use?
Here is an example: Consider a trucking company recently paying heavy fines due to discrepancies between recorded time and actual driving hours. Discrepancies like driver error, system malfunctions, or sometimes even complex regulations can lead to heavy financial and serious reputational consequences. This is where a tachograph comes in use as it helps monitor and record drivers’ activities and driving time accurately.
So, together let’s unfold the A-Z of tachographs- from its definition, history, alternatives and more.
Let’s start with the basics i.e. unfolding the meaning of tachographs.
What is a Digital Tachograph?
A digital tachograph is an electronic device installed in commercial vehicles, such as trucks and buses, to record information about the vehicle’s speed, distance traveled, and the driver. activity status. It replaces the old analog tachographs and is used primarily to ensure compliance with regulations regarding drivers’ HOS and rest periods.
Moreover, digital tachographs help store data on driver behaviour and activity, including driving hours, breaks, and rest periods, and they help fleet operators monitor and manage compliance with legal requirements related to road safety.
Stoneridge Electronics SE5000, Actia SmarTach, and Efkon Efas 3 / Intellic Efas 4 are a few popular digital tachograph head models that are best-selling in the market.
| 💡Fun Fact
The word tachograph is derived from the Greek word Tachos which means speed and graphos which means to write. |
Key Features of Digital Tachographs
- Driver Identification – Tachographs securely log and verify driver identity using a driver’s card.
- Data Storage – Helps in capturing and storing detailed driving and resting periods for legal compliance.
- Real-time Monitoring – Tachographs also help in providing instant access to vehicle speed, distance, and driver activity in real time.
- Downloading Data – Digital tachographs have streamlined downloading data, as they allow for easy transfer of stored data to external systems like telemetry or fleet management systems for detailed analysis and reporting.
History of Digital Tachographs (The Journey from Analog to Digital)
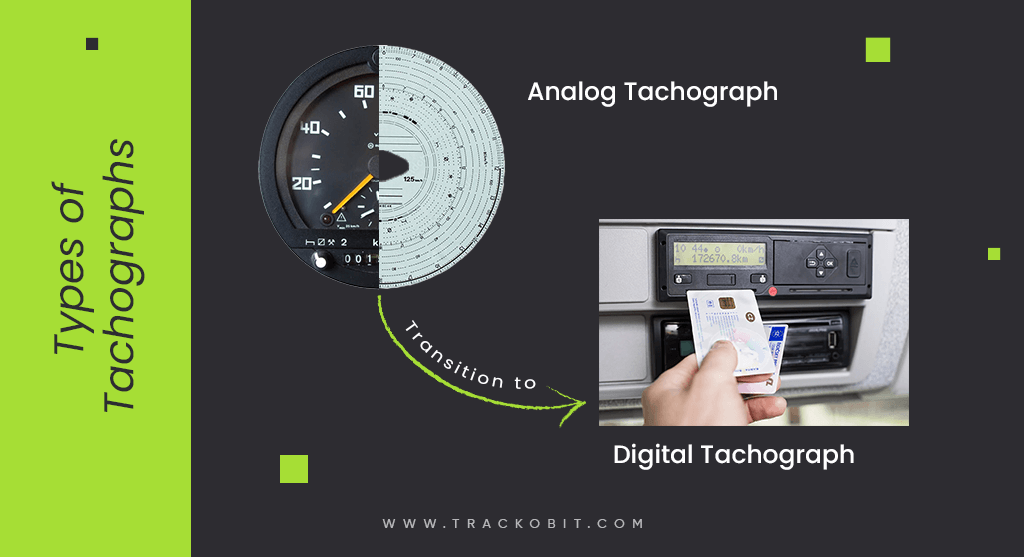
Different Types of Tachographs
By the heading itself, you might have understood tachographs come in two types i.e. analog and digital. The European Union introduced analog tachographs in 1985. It was in May 2006, when analog tachographs were replaced with digital ones.
The switch from analog to digital tachographs was driven by the need for improved accuracy, security, and tamper-proof data recording. That’s not all, it also helped enhance compliance with increasingly stringent EU regulations on driving hours and road safety.
Introduction of Analog Tachographs
When we talk about the introduction of analog tachographs, it is considered the earliest version of tachographs. In 1952, Germany made such devices mandatory for vehicles over 7.5 tonnes. Managing these devices was a constant struggle as recording data using a disc required manual input from the driver’s end. All this often led to the risk of clerical errors.
Some of the most common errors included drivers forgetting to record rest periods, making mistakes when filling out the paper chart, and much more.
That’s just not all, the build of the device was also full of imperfections. The source disc failed to reflect correct driving data as the wax disc beneath it was incapable of registering correct data.
Transition to Digital Tachographs
Digital tachographs have widely replaced analogs, as they have more advanced features and involve less manual tasks. The digital tachograph records driving time, rest periods, speed, and distance. Highlighting its advanced features, we can say the digital one has more enhanced data security and has tamper detection features, which further help in detecting and recording any attempts to manipulate the data.
To enable data recording via digital tachographs, drivers insert their driver card into the device before starting/finishing the trip.
New Smart TachoGraph
How to Use a Digital TachoGraph (Unfolding Steps)
Using a digital tachograph might seem confusing when you are just a beginner But with proper training and guidance, it becomes really easy to use. Here are some steps:
Step 1:
The very first step is about inserting your driver’s card. Drivers insert the card into the designated slot. The card must be inserted upside down with the chip facing upwards. Further, the tachograph authenticates the card and displays the driver’s name and other important info.
Step 2:
Once the driver has logged in, the tachograph asks some questions on the screen that are supposed to be answered. These questions can be about the last driving session, their rest periods, speed, and more.
Step 3:
Once the driver card is inserted and the previous data is confirmed, the next crucial step for the driver is to select their activities on different tachograph modes. They can decide when to drive, rest, load or unload the vehicle. This ensures that your drivers’ activities are accurately recorded and in compliance with legal requirements.
The Best Part?
The time interval for performing a specific routine related to driving, resting, and hauling or unloading the vehicle is already mapped on the digital tachograph solution. An alarm will ring whenever drivers are found under or overdriving or resting for prolonged periods.
Step 4:
Once the trip has started, the tachograph device in the background continues to record the recording driving time, speed, and other relevant data.
Step 5:
In situations of taking breaks and rest periods, the drivers need to ensure that they switch the activity status on the tachograph to “rest”. This becomes crucial for maintaining accurate records and complying with HOS (hours of service) regulations.
Overall, by following the above steps, drivers can ensure that their driving hours and activities are accurately recorded or not. This also helps them stay compliant with legal requirements and contribute to safer road conditions.
Shedding Some Light into Smart TachographsThe first generation of smart tachographs was introduced in June 2019. This enhanced the capabilities of digital tachographs. Smart tachographs use functionalities such as GNSS positioning that support real-time vehicle tracking and monitoring. The second generation of smart tachographs has been mandatory since August 2023. This new version of digital tachographs incorporates more sophisticated anti-tampering techniques and enhanced functionalities specifically aimed at ensuring compliance with EU regulations regarding cabotage and the posting of workers. Notably, the second generation will also facilitate the automatic recording of border crossings and the vehicle’s position during loading and unloading operations, further streamlining enforcement efforts and tachograph compliance. |
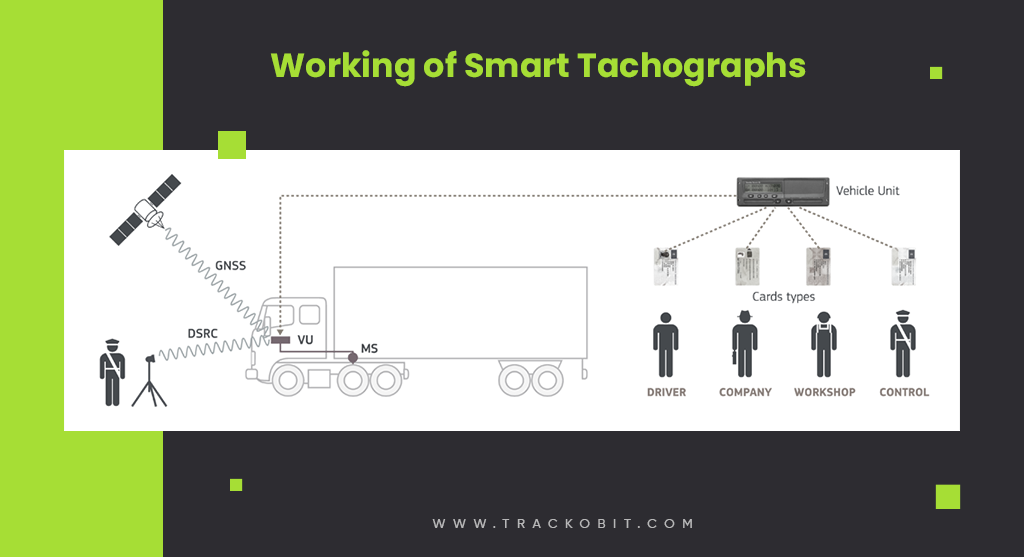
Working of Smart Tachographs
Different Types of Tachograph Cards
Now that you know everything crucial about tachographs, let’s dive into the several types of tachograph cards, each serving a different purpose-
| Card Type | Issued To | Main Function |
| Driver Card | Individual drivers | Records driver’s working hours and activities |
| Company Card | Transport companies | Allows access to data from all vehicles and drivers |
| Workshop Card | Authorized workshops | Used for calibration and maintenance of tachographs |
| Control Card | Enforcement authorities | Used for inspections and compliance checks |
| Smart Card | Fleet drivers | Enhanced features for security and data integrity |
Some Other Alternatives to Digital Tachograph
When it comes to fleet management, ensuring compliance, efficiency, and safety becomes really important. Tools like the digital tachograph have been indispensable in monitoring driver activity, recording hours of service, and ensuring compliance with regulations. However, as technology advances, many new alternatives offer better functions and data-driven insights.
These alternatives are not only complementary but some can be used as better alternatives for digital tachographs. Below are some of the best alternatives to the system.
1. Telematics System
We all know how telematics has amped up the game of visibility especially when it comes to fleet management. These systems bring a lot to the table – from real-time tracking, driver behavior monitoring, alerts on maintenance, and a lot more.
Telematics is a solution that integrates GPS technology with onboard diagnostics to monitor vehicular movements, driver behavior, and vehicle status in real time. It collects and transmits a wealth of data, including speed, location, engine diagnostics, and even the consumption of fuel. This ample data allows for a more detailed analysis of fleet of fleet operations.
Take a closer look- What is Telematics? An Introduction to Smart Vehicle Tracking
2. Driver Apps
Driver applications are mobile applications specifically designed for drivers to streamline their daily tasks and maintain better communications with fleet managers. These apps help drivers with attendance mark-ins, log driving hours, have access to their assignments, provide real-time updates on vehicular status, and maintain eDVIRs easily. These apps simply get integrated with other systems like telematics solutions for having a more holistic approach to fleet management.
3. Vehicle Data Loggers
On the next vehicle, data loggers are also one of the best alternatives to digital tachographs. These are devices installed in vehicles to record a wide range of data. Vehicle data loggers can cover data on vehicle performance, identify maintenance needs, and also improve driver behavior.
All-in-all, vehicle data loggers provide a more detailed and comprehensive view of vehicle operations compared to traditional methods, enabling better decision-making and fleet optimization.
4. In Cab Video Systems
In-cab video systems aka video telematics systems help enhance safety and compliance by providing visual records of driving activities. Video telematics systems capture footage of both the driver and the road. The systems help offer critical evidence in case of mishappenings and help to monitor driver behavior more closely.
The system makes safety a priority and streamlines incident management by providing clear footage combined with telematics data. With the help of this data and visuals, fleet managers can quickly determine fault, protecting drivers from false claims and minimizing legal costs. Moreover, fleet managers can also expect improved driver performance and maximize operational efficiency.
Take a deep dive into the technology- What Is Video Telematics | How Does Video Telematics Work
Let’s see how TrackoBit can change the game of fleet management for you.
TrackoBit offers a robust platform that integrates multiple fleet management tools, providing a comprehensive solution. Our software is integrated with telematics systems offering real-time tracking, driver behavior monitoring, and vehicle diagnostics.
Intrigued?
Other Trending Reads
- What are DTC Codes? Types & How to Decode Them
- Vehicle Management System – How Do They Work
- How to Track Vehicles Without GPS Tracking Devices?
FAQs on Digital Tachograph
-
What is a digital tachograph?
A digital tachograph is an electronic device used in vehicles to record driving time, speed, and distance to ensure compliance with road safety regulations.
-
How does a digital tachograph work?
It records data automatically through a driver’s smart card and vehicle unit, tracking driving hours, rest periods, and speed.
-
How long is digital tachograph data stored?
Data is stored in the vehicle unit for up to a year and on the driver’s card for 28 days.
-
What are tachograph modes?
Tachograph modes are settings that allow drivers to record different types of activities, such as driving, resting, loading/unloading, and other work-related tasks.
-
What are the different types of tachograph cards?
Tachograph software supports a variety of cards such as driver cards, company cards, workshop cards and more.
-
Who is required to use a digital tachograph?
Drivers of commercial vehicles weighing over 3.5 tons or with more than nine seats in the EU are required to use a digital tachograph.
-
Can I manually enter data into a digital tachograph?
Yes, drivers can manually input activities like rest periods or work done outside the vehicle.
-
What is Tachograph Software?
Tachograph software is a tool designed to manage data that is fetched by the tachograph. This helps in adhering to tachograph compliance with driving regulations.
Anvesha is a communication specialist at TrackoBit. With a strong background in media and communications, she adds much-needed balance and brevity to TrackoBit’s... Read More
Related Blogs
-

5 Best Driver Behavior Monitoring Systems for 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 23, 2026Having the best driver behavior monitoring system is a necessity as it helps you ensure driver safety and optimize operational…
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.