-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is a Telematics Control Unit? Benefits & How It Works
- Author:Anvesha Pandey
- Read Time:7 min
- Published:
- Last Update: September 10, 2024
Table of Contents
Toggle
Unfold the what, why, and how of telematics control units. From its workings to understanding the difference between TCUs and TGUs- everything, so get started.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Do you ever wonder how modern-day vehicles communicate where they are, how fast the speed is, or how safe the driving is?
Well, the answer lies in Telematics Control Units (TCUs).
In the next 5 min for you:
|
What is a Telematics Control Unit?
A telematics control unit is an embedded system within a vehicle. It’s a central hub for collecting, processing, and transmitting data between vehicles and external networks.
It integrates with various communication technologies, such as GPS, cellular networks, and Bluetooth. This enables real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and control of vehicle systems.
A telematics control unit is made up of the following components
- Microcontroller/Processor
- GPS Module
- Cellular Modem
- Memory/Storage
- SIM Card
- CAN Bus Interface
- Bluetooth/Wi-Fi Module
- Power Management Unit
- Sensors
- Antenna
How Does the Telematics Control Unit System Work?
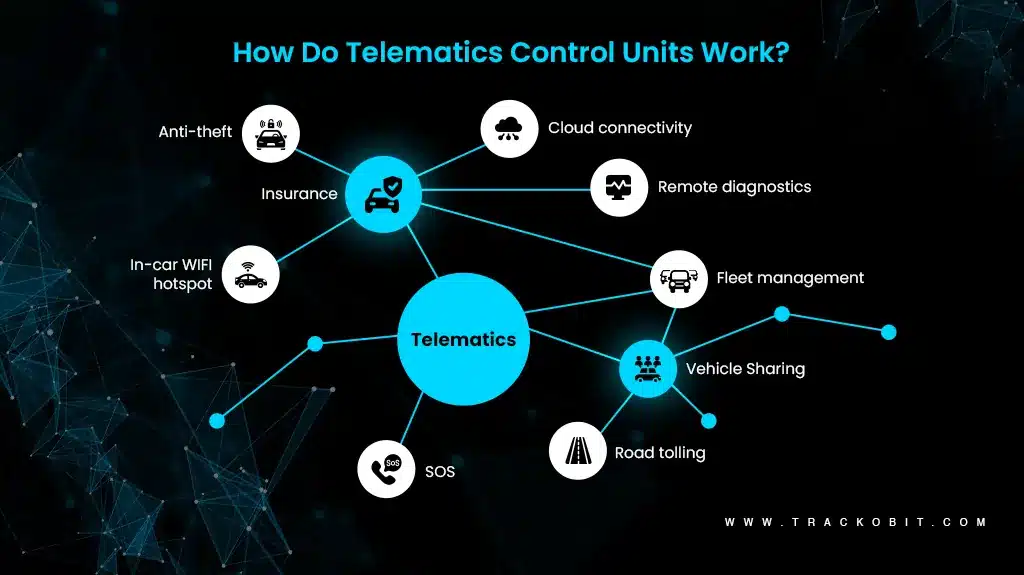
Wondering how telematics work? Explained here
The working of the Telematics Control Unit (TCU) involves multiple steps. Every step of the system contributes to the overall functionality. Here is a breakdown of how the system typically works.
STEP 1- DATA COLLECTION
The telematics control unit collects data (like speed, engine performance, fuel levels, GPS location, and more) from various vehicle sensors and internal systems. This includes gathering information from sensors connected to the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus, such as speed, engine performance, fuel levels, and tyre pressure.
STEP 2- DATA PROCESSING
Once the data is collected, the telematics control unit processes the data using the microcontroller. It is the same step in which raw data is filtered and converted into actionable insights.
A telematics control unit can calculate the vehicle’s route efficiency, monitor engine diagnostics, or determine if the vehicle requires maintenance. This processing helps in making real-time decisions that can improve vehicle performance and safety.
Seems complicated? Let us simplify this with an example: If the engine of your vehicle gets too hot, the telematics control unit will recognize that this can be a serious concern in the future and will shoot an alert accordingly.
STEP 3- DATA STORAGE
Once the data is processed, it needs to be stored. This processed data is stored within the TCU’s memory. Memory is typically divided into two types: volatile (which means temporary) storage and non-volatile (which means permanent storage).
The volatile memory is used for the immediate processing of data, whereas the non-volatile one holds critical data such as logs, diagnostics, and historical vehicle performance.
STEP 4- DATA TRANSMISSION
The TCU communicates the processed data to the external networks or devices through a cellular modem. This transmission can take place in real-time, allowing the fleet managers to closely have an eye on the vehicle’s status remotely.
Note:- In case of the absence of a cellular modem, TCUs also transmit data via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi for short-range communication.
STEP 5- INTEGRATION
The telematics software often integrates with other in-vehicle systems and other platforms like fleet management platforms to enhance its functionality. This includes connecting with the vehicle’s infotainment system, driver assistance technologies, or even external services like emergency response or traffic management systems.
By working in concert with these systems, the TCU enables a connected and automated driving experience, supporting features like navigation, safety alerts, and driver behavior monitoring.
Now that you know how the telematics controls work, let’s have a sneak peek into how the systems help in real-time monitoring and shoot alerts.
| 📌How does TCU Help in real-time monitoring and send actionable alerts?
Well, in simple words the telematics control unit (TCU) plays a very important role in real-time monitoring and the delivery of actionable insights. This happens by gathering and analyzing data from the vehicle systems. Let us break this down into three steps and understand how this actually works.
The TCU continuously monitors the vehicle’s status and environment throughout its operations.
Now in case of any anomalies like sudden deceleration, engine faults, or a deviation from the planned route—the TCU can immediately trigger alerts. Now the question arises to whom and where are these alerts prompted? These alerts are sent to either the driver or fleet managers. |
Why is Telematics Control Unit Important?
Now that we know so much about telematics control modules, you might be wondering what’s important for a telematics control unit.
The telematics control unit (TCU) is crucial for many reasons, making it an important component, especially for modern vehicles within the context of connected vehicles and fleet management-
1. Enhances Vehicle Safety
There’s no doubt that TCUs improve the safety of vehicles by monitoring various vehicle parameters and driver behavior in real time. The system can detect issues such as engine malfunctions, tire pressure anomalies, or aggressive patterns, and then provide immediate alerts to the driver or fleet managers.
2. Promotes Real-Time Tracking
One of the primary functions of a TCU is real-time tracking. This allows fleet managers to know the precise location of their vehicles at any time. This capacity is particularly important for logistics and transportation companies, as it helps optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve the overall fleet.
Moreover, telematics control unit help a lot in cases of vehicle theft, and the TCU’s tracking ability is invaluable for recovery efforts.
3. Facilitates Predictive Maintenance
The TCU’s ability to continuously monitor vehicles’ health facilitates predictive maintenance. The system can predict when a part is likely to fail or when maintenance is needed by analyzing data such as engine performance, fluid levels, and brake condition.
This proactive approach further helps reduce the likelihood of breakdowns, minimizes downtime, and extends the lifespan of the vehicle.
Wondering how:- Suppose the telematics control unit in your vehicle detects any kind of unusual vibrations in the engine, it will predict a potential failure in the fuel pump as it has a high chance of breaking soon. This further initiates a prompt alert to check and replace the pump before something escalates.
4. Facilities Connected Vehicle Ecosystems
As vehicles become more connected, the TCU serves as the central hub for communication with external networks and devices. This enables features such as over-the-air software updates, remote diagnostics, and integration with smart city infrastructure.
This connectivity supports a wide range of applications, from infotainment services to vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, paving the way for future innovations in autonomous driving and smart transportation.
Difference Between Telematics Control Units (TCUs) & Telematics Gateway Units (TGU)
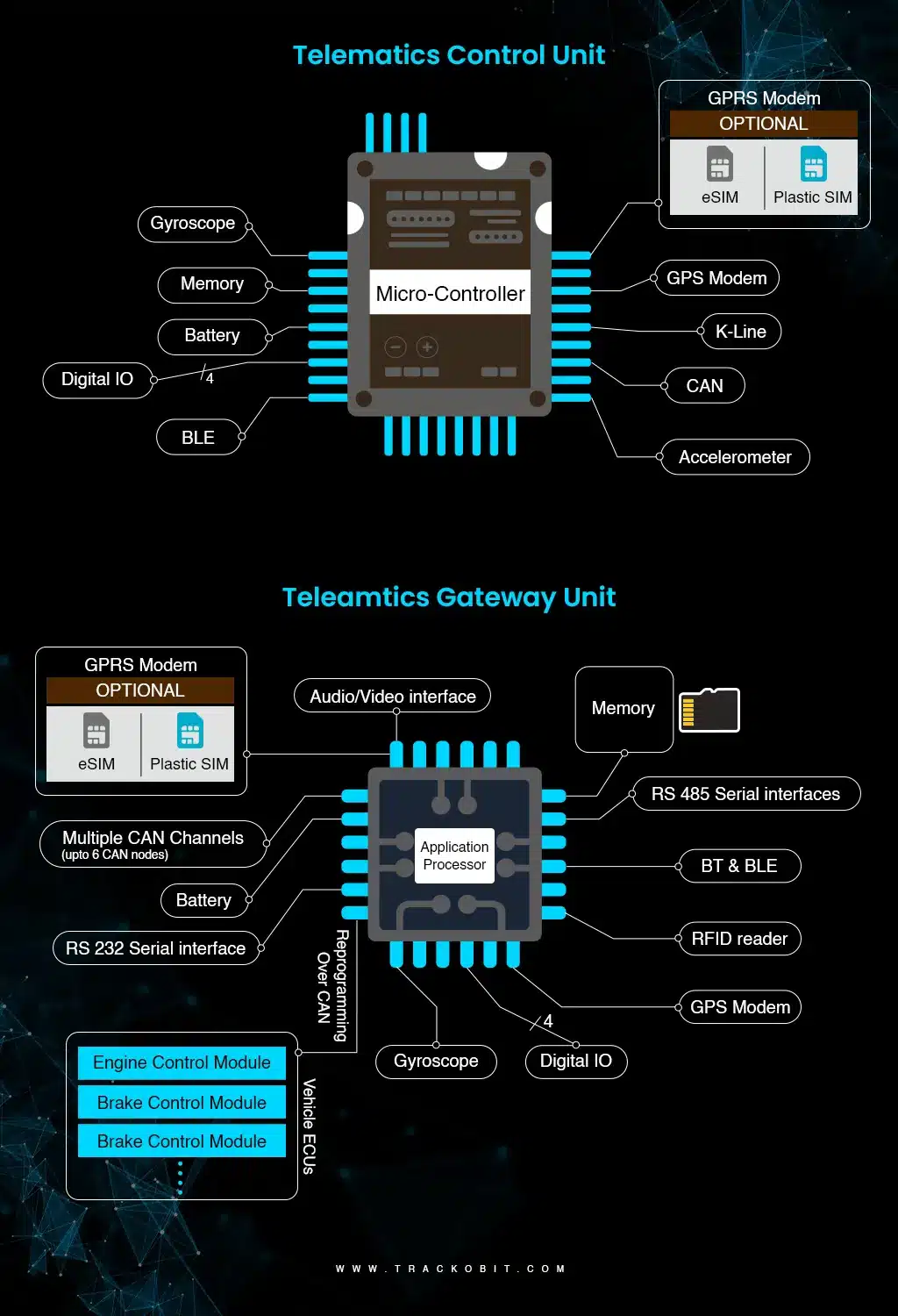
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the various components of TCUs and TGUs
By now, you would have surely understood that telematics serves as the digital backbone, connecting vehicles to a vast network of information.
Most of us often need clarification on two crucial components i.e. Telematics Control Units (TCUs) and Telematics Gateway Units (TGUs). While they might sound similar, they play distinct roles. The table below explains this better
| Features | Telematics Control Unit (TCU) | Telematics Gateway Unit (TGU) |
|
Collects, processes, and transmits vehicle data to a remote server. | Acts as a communication hub, connecting multiple devices/systems. |
|
Directly collects data from vehicle sensors. | Aggregates data from various devices (e.g., sensors, TCUs). |
|
Transmits data via cellular networks or satellite. | Facilitates communication between devices and external networks. |
|
Integrated with vehicle systems (e.g., ECU, GPS) | Connects different telematics devices, including control units. |
|
Used in individual vehicles for monitoring and diagnostics. | Used in fleets that collect multiple data from various units. |
|
Vehicle management, usage-based insurance. | Fleet coordination, remote diagnostics, IoT applications |
Overall, TCUs ( telematics control units) focus mainly on in-vehicle data collection and real-time functionalities, whereas TGUs (telematics gateway units) often manage transmission, integration, and communications between the vehicle and external systems (cloud platforms, fleet management systems, or more).
The Amped Version of Telematics Systems- Video Telematics System
We all know the fact that technology tends to grow and how telematics has replenished in a thousand different ways. From AI powdered predictive analysis to ADAS integration to enhanced connectivity and IoT of course, you can see how telematics has grown.
Out of these many advancements, one such advancement is video telematics.
Wondering what technology?
Let’s break this down for you.
Well, Video telematics is a technology that involves the use of cameras and sensors to provide better insights into the driver’s behavior. This involves capturing both the in-cabin and outside-driving patterns. This data is just not used for generating alerts or notifications for inappropriate events or driving patterns but is also used for driver safety and risk management.
Here’s how the system works with an example: If the system detects dangerous driving patterns, it immediately sends an alert to warn/alert the driver. In spite of this, if the driver continues the same inappropriate Behaviour, this data is sent to the respective fleet manager. This helps the fleet manager or the assigned authority to get in touch with the driver to rectify the situation.
Video telematics software provides you with ample benefits, some of which are listed below-
- Reduced risk of accidents
- Better management of the fleet
- Diver and consignment safety
- Hassle-free insurance claims
Since technology promises to evolve in the future, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of advanced video telematics solutions. For instance, you can consider expecting advanced analytics techniques to be used to extract valuable insights such as identifying potential road hazards or predicting traffic congestion.
Moreover, the integration of video telematics with other technologies, such as autonomous driving, could lead to even greater benefits in terms of safety and efficiency.
📌Get detailed insights into Video Telematics- What Is Video Telematics | How Does Video Telematics Work
Planning to Invest in Video Telematics Solutions- TB can be your Partner
Well, now that you know the ample benefits of the system, you must surely be wondering why not get your hands on the right solution, TrackoBit can be a great bet as we offer customized solutions to advanced video telematics technology. So if you are seeking a reliable technology partner to keep an eye on your fleet and expect enhanced visibility.
Let’s talk!
| 📌Some Technical Reads |
FAQs On TCUs
-
What is a Telematics Control Unit (TCU)?
A TCU is an embedded system in vehicles that collects and transmits data such as location, speed, and engine diagnostics to remote servers for fleet management and vehicle monitoring.
-
What are the benefits of using telematics solutions?
TCUs improve fleet efficiency, enhance driver safety, provide real-time vehicle diagnostics, and reduce operational costs through better maintenance planning.
-
How secure is the data transmitted by a TCU?
TCUs use encryption and secure communication protocols to protect data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
-
Can TCUs be used for insurance purposes?
Yes, TCUs can provide data for usage-based insurance, where premiums are calculated based on driving behavior and vehicle usage.
-
How do telematics control devices work?
It uses GPS and cellular networks to gather and send real-time data from the vehicle to a central system, enabling tracking, diagnostics, and communication.
-
Can telematics software be installed in all vehicles?
While most modern vehicles can support TCUs, older models may require additional hardware or may not be compatible at all.
-
What is the role of a TCU in fleet management?
TCUs provide fleet managers with real-time visibility into vehicle location, driver behavior, and maintenance needs, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
Anvesha is a communication specialist at TrackoBit. With a strong background in media and communications, she adds much-needed balance and brevity to TrackoBit’s... Read More
Related Blogs
-

5 Best Driver Behavior Monitoring Systems for 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 23, 2026Having the best driver behavior monitoring system is a necessity as it helps you ensure driver safety and optimize operational…
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.