-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What are RFID Tags? Benefits, Use Cases & How They Work
- Author:Tithi Agarwal
- Read Time:10 min
- Published:
- Last Update: October 8, 2024
Table of Contents
Toggle
RFID technology is emerging as a transformative force. It facilitates wireless data transfer through radio waves and offers multiple applications across sectors and industries.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags are rapidly becoming an industry favorite. They automate and enhance supply chain visibility and tracking across different sectors.
Surprisingly, many are still not fully aware of how these tags work and their application in different industries and sectors. In this article, we will take a closer look at what RFID tags are, how they work, and some of the ways in which they are being used today.
What are RFID Tags?
RFID tags are a type of tracking system that uses smart barcodes in order to identify items. It is short for “radio frequency identification,” as it utilizes this technology.
These radio waves transmit data from the tag to a reader, which then transmits the information to an RFID computer program. RFID systems usually contain RFID readers, tags, and antennas.
They are widely used in industries such as healthcare, retail, hospitality, and manufacturing. RFID is like barcodes but is not restricted by line-of-sight.
An RFID tag may also be called an RFID chip.
3 Types of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Tags
Here are 3 common types of RFID tags:
1. Active RFID tags
Active RFID tags rely on their own power source to transfer the information to RFID readers. These tags typically have small batteries that need to be replaced periodically. The advantages of active RFID tags are that they offer long communication ranges and continuous tracking.
Additionally, they can initiate communication on their own. Such tags are used to perform diagnostics and high-precision activities.

Types of RFID Tags
2. Passive RFID tags
Passive RFID tags, on the other hand, do not have their own power source. They depend on the electromagnetic energy emitted by RFID readers to transmit data. These tags are cost-effective and last longer than active RFID tags. However, they do not have very long communication ranges and are suitable only for day-to-day tasks such as inventory management, retail tagging, toll collection, etc.
3. Semi-passive RFID tags
Semi-passive RFID tags have batteries but communicate with RFID readers using electromagnetic energy, just like passive RFID tags. These tags are very similar to passive tags in terms of sizing and appearance. However, because of their in-built batteries, they have longer communication ranges (860 MHZ—960 MHz range). Semi-passive RFID tags have applications in logistics, IT, and healthcare industries.
What are RFID Readers?
An RFID reader is the brain of the RFID system. Readers, also called interrogators, are devices that transmit and receive radio waves to communicate with RFID tags. In terms of mobility/flexibility, RFID readers are typically divided into three distinct types: Fixed RFID Readers, Mobile RFID Readers, and USB Readers.
- Fixed RFID readers are stationary devices mounted on walls, desks, or portals and can connect to 1-8 antennas. With multiplexers, they can support up to 64 antennas, depending on coverage needs. Small applications require one antenna, while larger areas may need multiple antennas for full coverage.
- Mobile RFID readers are handheld, battery-powered devices that transmit data using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. They fall into two types: Mobile Computing Devices with onboard computers and Sleds that connect to smart devices. Integrated readers with built-in antennas are common for mobile readers with low-traffic indoor applications.
- USB Readers are a unique subset of RFID readers because, while they are fixed to a computer, they are not fixed to a wall outlet. Allowing them to have more mobility than a typical fixed RFID reader. USB readers are incredibly popular for any desktop application or specifically for reading and writing individual RFID tags.
How does RFID Work?
An RFID tag transmits and receives information via an antenna and a microchip—also sometimes called an integrated circuit or IC. The microchip on an RFID reader is written with whatever information the user wants.
At a simple level, RFID systems consist of three components: an RFID tag or smart label, an RFID reader, and an antenna. RFID tags contain an integrated circuit and an antenna, which transmit data to the RFID reader (also called an interrogator). The reader then converts the radio waves to a more usable form of data.
Information collected from the tags is then transferred through a communications interface to a host computer system, where the data can be stored in a database and analyzed at a later time.
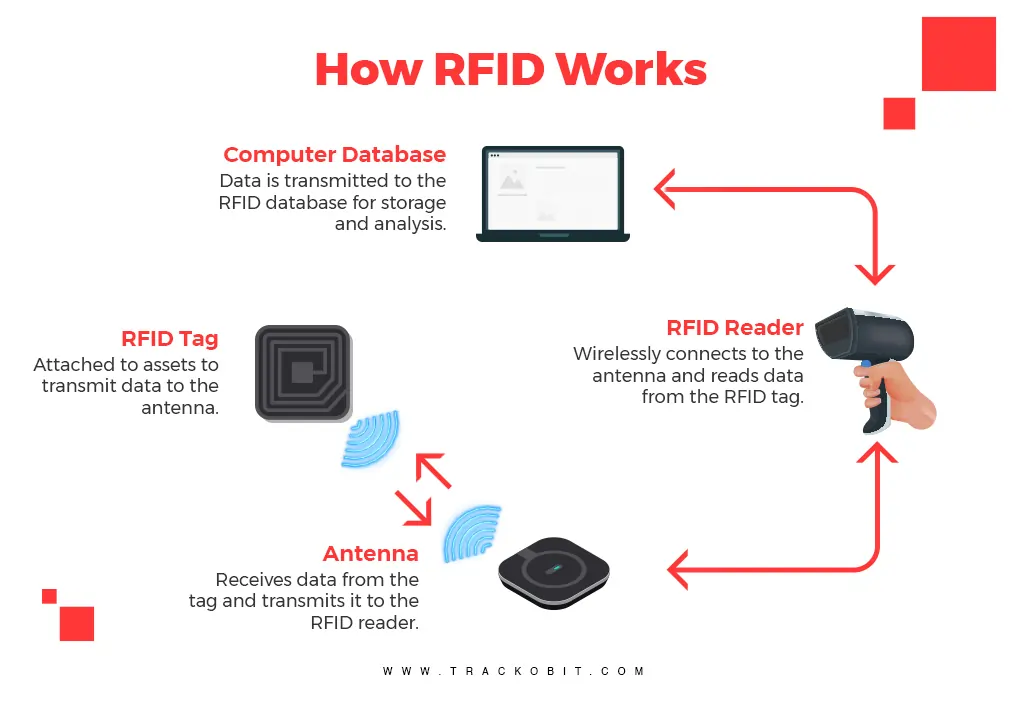
How RFID Works
What Are the Benefits of Using RFID to Track Assets?
A rise in consumer and stakeholder demands has solidified the need for asset-heavy businesses to deploy effective asset-tracking solutions. No matter what size, type, or industry your business is categorized in, all objectives are relatively similar when it comes to the management of assets. You need a tracking system that is going to:
1. Reduce Loss and Theft of Assets With Real-Time Tracking
Replacing assets that have either been lost, misplaced, or stolen can damage a business’s bottom line. This is a common expense across most asset-heavy industries. The American Auto industry replaces lost reusable packaging for $750 million a year, whereas job site theft costs Construction companies $1 billion annually.
Did you know that in 2016, 24 million luggage articles were lost due to poor location tracking.
By implementing multiple RFID readers and antennas, businesses are able to triangulate the exact whereabouts of their assets. Resulting in real-time and accurate location data. In addition to reducing replacement costs, a GPS tracking system helps reduce the manual process of locating assets and wasting hours.
2. Reduce Costs and Time Through Automation
The use of RFID to track assets, whether in transit or in warehouses, allows businesses to monitor the movement of goods automatically.
The data collection process is also automated, allowing businesses to receive accurate updates in real time straight to an asset tracking system. From here, asset managers can monitor stock levels, track the supply chain, and even identify costly operations delays.
This eliminates the need for manual tracking methods such as spreadsheets. This effectively reduce employee labor time and human intervention.
3. Provide a Good Return On Investment (ROI)
A relatively cheap set of tools is needed to deploy an effective RFID tracking system that allows businesses of all revenues to access it. This enables enterprises with multiple sites and warehouses to install RFID and small and medium businesses.
RFID is a long-lasting and cost-efficient solution compared to other forms of asset tracking. Its cheap running costs have enabled businesses in the Manufacturing, Logistics, and Retail sectors to achieve an ROI of up to 200%.
Modern smartphones are equipped with RFID reader capabilities, eliminating the need to purchase an expensive device. Not to mention the durability of a plastic tag that can be used over and over again.
Industry Use Cases of RFID Sensors
The primary advantages of RFID technology include seamless data transfer and automation. It can help simplify day-to-day tasks, such as retail billing, supply chain management, detecting security breaches, toll collection, etc. Let’s discuss some of the significant applications of RFID technology in detail:
1. Toll Payment Collection at Toll Plazas
RFID technology serves as a streamlined solution for toll payment collection on a global scale, offering an efficient alternative to the time-consuming and tiring manual methods. The Government of India implemented the FASTag system for toll collection at national highway toll plazas nationwide.
Nearly all toll plazas on national highways are equipped with FASTag readers for electronic toll transactions through RFID FASTags affixed on the windscreens of cars, buses, trucks, etc.
So how this happen?
The FASTag incorporates a microchip that securely stores data related to the vehicle and its owner. These tags are linked to payment wallets, facilitating seamless funds transfer directly to the toll collection agency’s bank account.
2. Logistics and Supply Chain Management
RFID tags significantly improve long-haul logistics by offering real-time tracking, better asset management, and enhanced security. They allow companies to monitor the location of vehicles and shipments in transit, providing continuous updates through RFID readers at checkpoints. This real-time visibility helps logistics managers ensure shipments are on track, optimize delivery routes, and respond quickly to delays or disruptions.
RFID tags also automate inventory management, reducing the need for manual checks at loading and unloading points. This speeds up operations and minimizes errors, ensuring the right goods are loaded onto the correct trucks or shipping containers. Additionally, RFID helps track high-value assets, such as trailers or containers, reducing theft or loss during long-haul trips.
Furthermore, RFID data aids in better planning for the maintenance of transport vehicles by tracking their usage, ensuring timely service. Overall, RFID improves operational efficiency, reduces transit times, and increases transparency throughout the logistics process, leading to cost savings and better customer satisfaction.

RFID technology
3. Construction Sites
Construction sites are often spread over large areas, with multiple teams working simultaneously. RFID tags, when attached to equipment and machinery, allow site managers to track their exact location in real time. This ensures that equipment is where it should be and minimizes downtime spent searching for tools or machinery.
RFID tags enhance construction site efficiency by tracking equipment and heavy machinery in real-time. This reduces time wasted searching for tools, optimizes resource allocation, and ensures that the right equipment is available when needed.
RFID also improves asset management by preventing loss or theft and enabling automated inventory checks. RFID tracks usage patterns for maintenance, ensuring timely machinery servicing to avoid breakdowns.
Additionally, RFID enhances site safety by verifying that only authorized personnel operate specific machinery, reducing accidents.
4. Medical Equipment Monitoring
RFID technology plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry as well. It has the potential to streamline the monitoring of medical equipment, tracking of patients, and managing medicine inventory. It can also restrict entries for unauthorized personnel in sensitive zones.
Adopting RFID systems in healthcare removes the need for physical scanning, thus enhancing the efficiency of various medical procedures. Additionally, it helps minimise the risk of human errors during procedures, contributing to higher patient satisfaction. The implementation of this technology enables healthcare facilities to reduce patient wait time, specifically during critical situations.
5. Access Control and Security
RFID Technology is widely employed for access control and security applications, providing a convenient and secure way to manage entry to buildings, offices, airports, hospitals, parking lots, and restricted areas.
The entry gates are fitted with RFID readers, and only authorized personnel are given ID cards equipped with RFID tags. When an unauthorized person without an RFID tag tries to cross the entry gate, the RFID readers detect foul play and start a buzzer or alarm to alert the authorities.
What are the Top Reasons for Using RFID
- Increased efficiency: RFID tags can be read quickly and accurately, allowing for faster and more efficient tracking of items.
- Improved accuracy: Unlike barcodes, RFID tags do not require a direct line of sight to be read, which means they can be read even when hidden or obscured.
- Reduced labor costs: RFID tags can be read automatically, eliminating the need for manual scanning and reducing labor costs.
- Enhanced security: RFID tags can be encrypted and programmed with unique identifiers. Making it more difficult for counterfeit or unauthorized items to enter the supply chain.
- Real-time tracking: RFID tags can provide real-time data on the location and movement of items, allowing for better inventory management and supply chain optimization.
- Durability: RFID tags are typically more durable than barcodes, which can become damaged or unreadable over time.
What is the Difference Between RFID vs. Barcodes
RFID, as an alternative to barcodes, is increasingly being used. RFID and barcode technologies are used similarly to track, but they have some important differences.
RFID Tags |
Barcodes |
| Can identify individual objects without direct line of sight. | A direct line of sight is required for scanning. |
| You can scan items from inches to feet away depending on the tag type and reader. | Require closer proximity for scanning. |
| Data can be updated in real-time. | Data is read-only and can’t be changed. |
| Require a power source. | No power source is needed. |
| Read time is less than 100 milliseconds per tag. | Read time is half a second or more per tag. |
| Contains a sensor attached to an antenna, often contained in a plastic cover, and is more costly than barcodes. | Printed on the outside of an object and more subject to wear. |
Conclusion
Integration of RFID into operations across industries and sectors can be beneficial. For example, supply chains can enhance the visibility of their inventory, asset location, and consignment safety.
TrackoBit, a vehicle tracking software, also contributes to this technology. It can easily transfer and analyze the transmitted data from the RFID tags and share real-time coordinates of the assets and consignment with the logistics company.
FAQS
-
What is an RFID tag used for?
RFID tags are used for transmitting data through radio waves. They have multiple applications across industries, such as logistics, healthcare, security, retail, and automobile.
-
Can RFID tags be tracked?
Yes, RFID tags can be tracked. They can be tracked automatically using active RFID tags or manually using passive RFID tags. To be tracked RFID tags provide data related to where they have been and where they currently are.
-
Can RFID tags track the location?
RFID tags themselves don't track location. However, RFID readers can detect their presence within a specific range, enabling proximity-based tracking but not continuous location tracking.
-
Where are RFID tags used?
RFID tags automate identification and improve operational efficiency in supply chain management, inventory tracking, retail, logistics, access control, and healthcare.
-
What is RFID sensor technology?
RFID sensor technology combines RFID with sensors to collect environmental data (e.g., temperature, humidity) along with identification, providing real-time information in logistics, healthcare, and supply chain.
-
What is RFID technology?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. It’s widely used for asset tracking, inventory management, and automation.
Tithi Agarwal is an established content marketing specialist with years of experience in Telematics and the SaaS domain. With a strong background in literature and industrial expertise in technical wr... Read More
Related Blogs
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.
-

Plug, Pair, Perform TrackoBit Introduces BLE Sensor Integration
Tithi Agarwal November 26, 2025TrackoBit’s BLE Sensor Integration enables wireless, real-time monitoring with faster installs and accurate insights. It improves fleet efficiency, visibility, and…

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.