-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
From Raw Data to Actionable Insights: The Role of CAN Bus in Fleet GPS Tracking
- Author:Tithi Agarwal
- Read Time:7min
- Published:
- Last Update: March 24, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle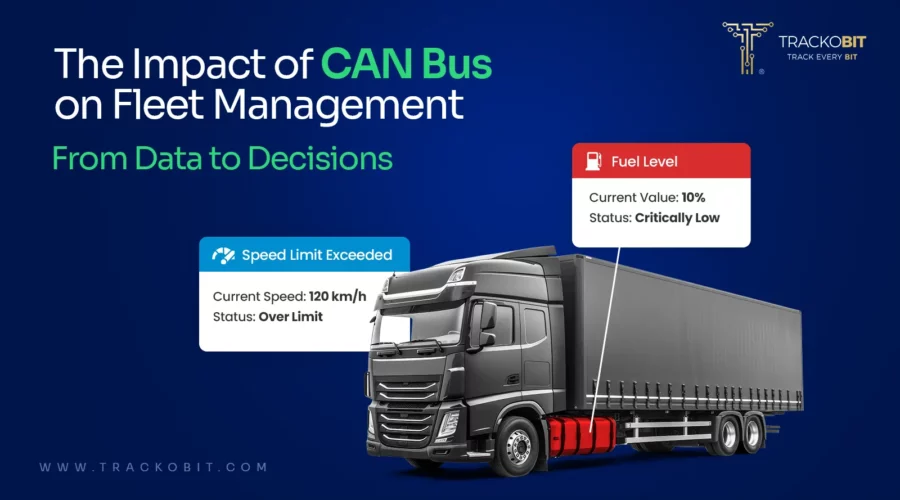
CAN bus data ensures unmatched accuracy, early error detection, and cost optimization, making fleet management more efficient and reliable.
Table of Contents
Toggle
From monitoring engine health to tracking fuel efficiency, CAN bus is the unsung hero behind modern fleet management.
Combined with GPS tracking and OBD-II data, it transforms raw vehicle data into actionable insights. Managers using fleet management software can now decode everything from driver behavior to engine performance in real-time. Making smarter decisions, reducing costs, and improving safety.
Let’s dive into how CAN bus improves fleet management!
What is the CAN Bus Protocol?
Modern vehicles come equipped with electronic control units (ECUs) and various other devices. But how do they communicate reliably? This is achieved through the Controller Area Network (CAN bus), a message-based protocol.
In this system, all devices receive messages or “frames” without the need for a host computer.
CAN offers exceptional control and fault detection capabilities, ensuring reliable data transmission. Errors are quickly identified, allowing information to reach its intended destination efficiently. This makes it a perfect protocol for managing complex systems with distributed control. Additionally, it minimizes wiring, reducing both costs and weight.
How Does CAN Messaging Work?
Devices connected to a CAN bus are referred to as “nodes.”
Each node consists of a CPU, a CAN controller, and a transceiver. The transceiver adjusts signal levels for both incoming and outgoing data. While all nodes can transmit and receive data, they do so at different times.
Rather than sending data directly to one another, nodes transmit information onto the network, making it accessible to the intended recipient. To ensure accuracy, all nodes are synchronized and sample data from the network simultaneously.
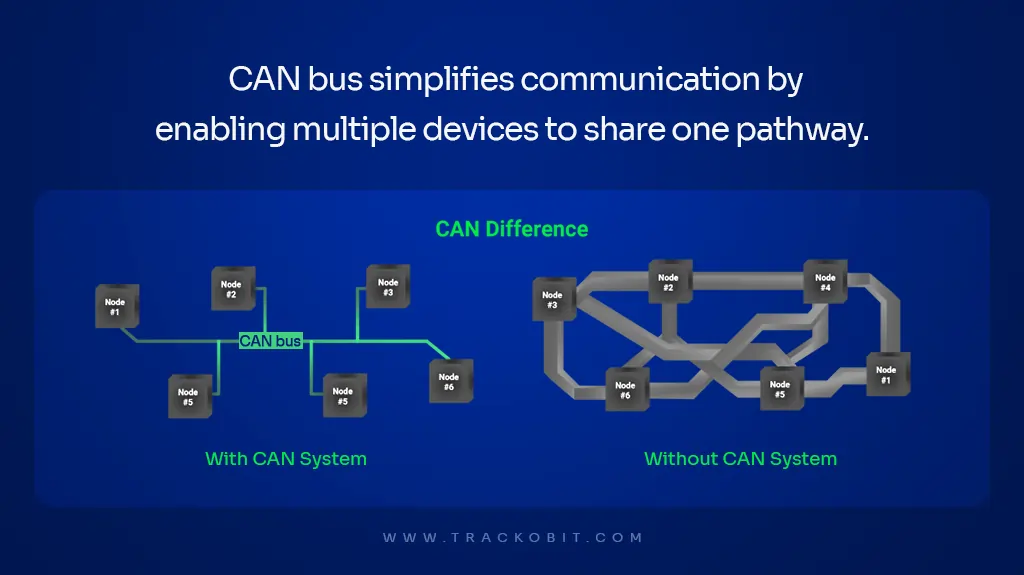
The CAN Bus lets multiple devices share a single data line for communication, reducing wiring, improving efficiency, and ensuring reliable data exchange.
This is getting too complicated and hard to understand, right?
Well to simplify it, you can imagine CAN messaging to work like a group chat where all connected devices like sensors, controllers and other vehicle parts can communicate with each other. They do not need a central server.
Here’s how it works in the simplest way:
- Common Chat Room – All devices are connected to the same “chat room” (CAN bus).
- Unique ID for Each Message – Every message sent has a unique ID, like a name tag.
- Broadcast System – When a device sends a message, all other devices “hear” it.
- Priority System – If two devices try to talk at the same time, the message with the lower ID gets priority (like raising your hand first).
- Smart Listening – Devices only respond to messages they care about. If it’s not relevant, they ignore it.
Example:
- The brake sensor sends a message saying, “Brakes applied!”
- The engine control module (ECM) hears it and reduces power.
- The dashboard display also hears it and shows a “Braking” warning.
So, CAN messaging is like a fast and organized group chat where everyone knows when to talk and what to listen to!
This structure allows for real-time, low-latency communication with high reliability and fault tolerance. These very reasons are why CAN is widely used in automotive and industrial systems.
Advantages of CAN Bus in Fleet Management
1. Real-Time Vehicle Monitoring
The CAN bus collects real time data from sensors and Electronic Control Units (ECUs). It transmits important parameters like speed, RPM, fuel level, engine temperature, and brake status. Fleet management software connected to the CAN network can decode this data and display it for live vehicle monitoring.
2. Predictive Maintenance
For predictive maintenance, the CAN bus sends diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) when it detects a fault or abnormal condition. It continuously monitors factors like engine load, coolant temperature, and oil pressure. This helps predict potential failures before they cause serious problems.
3. Driver Behavior Monitoring
The CAN bus also tracks driver behavior by recording actions like hard braking, rapid acceleration, and idling time. This data is sent to the fleet management system, which generates driver performance reports. If unsafe or aggressive driving is detected, alerts are triggered. This helps fleet managers coach drivers and improve safety.
4. Fuel Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Fuel efficiency can also be managed using CAN bus data. It monitors fuel consumption, throttle position, and engine load. By analyzing this information, fleet managers can spot excessive fuel usage caused by poor driving habits or mechanical issues, helping reduce costs.
5. Enhanced Safety and Compliance
Safety and compliance are enhanced through CAN bus tracking. It monitors seatbelt usage, brake response time, and tire pressure using connected sensors. If a safety violation occurs, such as an unfastened seatbelt, the system can send an alert to the fleet manager. Data on speed limits and safety protocols is also recorded for audits and driver training.
6. Remote Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
The CAN bus supports remote diagnostics through telematics devices. Fleet managers can access real-time sensor data and read DTCs from a central system. This allows them to troubleshoot issues remotely without bringing the vehicle to a workshop, reducing downtime.
How to Read CAN Bus Data
All these fabulous benefits a fleet-dependent business can reap with CAN . But how do they decode the CAN message? Here is how –
- Connect OBD-II Adapter – Plug an OBD-II adapter into the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- CAN Protocol Communication – OBD-II uses the CAN protocol to transmit vehicle data.
- Signal Conversion – The adapter captures raw CAN signals and converts them into readable data.
- Data Decoding – A CAN software decodes the messages, which include:
- ID – Identifies the source (e.g., engine, brakes).
- Data – Shows values like speed, RPM, and fuel level.
- Real-Time Monitoring – The software displays real-time values and alerts.
- Performance Insights – Helps monitor vehicle health and detect issues.
Different Types of CAN bus
There are multiple versions of CAN as defined by the ISO 11898 standard. But the most dominant ones are:
A) Low speed CAN
- Purpose: Used for non-critical systems.
- Speed: Up to 125 kbps.
- Use Cases: Diagnostics, dashboard controls, power windows.
- Advantage: More economical wiring.
B) High Speed CAN
- Purpose: Used for critical systems requiring fast updates and high accuracy.
- Speed: From 1 kbps to 1 Mbps.
- Use Cases: ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), airbags, engine control, electronic stability.
- Advantage: High accuracy and fast response time.
C) CAN FD (flexible data rate CAN)
- Purpose: Handles increasing data requirements in modern vehicles.
- Speed: Up to 8 Mbps.
- Data Capacity: Increased from 8 bytes to 64 bytes per message.
- Use Cases: Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous driving.
- Advantage: Higher speed and more data per message.
This brings us to…
TrackoBit’s Latest Update Makes CAN Data Mapping Effortless
TrackoBit has introduced a major update in its Sensor Management module, making CAN data mapping more flexible and user-friendly. This new development allows users to customize how CAN data is processed and displayed, eliminating previous limitations on supported parameters and device compatibility.
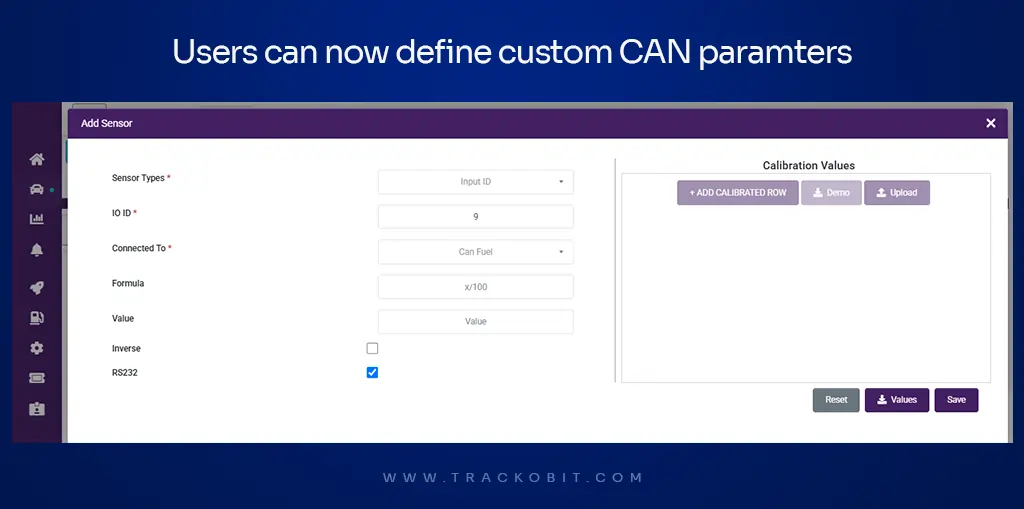
Now users can enter custom sensors on TrackoBit.
With this update, users can now add custom sensors with user-defined field names. CAN data is extracted from GPS packets received from vehicle trackers. The system identifies the position of CAN data within the packet, allowing users to map it directly through the Sensor Management module.
For example, if CAN odometer data is located in the 11th position of the packet, the user can create a custom sensor named “CAN Odometer” and assign it to position 11. Once mapped, the data will be available on both the dashboard and reports.
The customization options are highly flexible:
- Users can define the unit of measurement (e.g., meters or kilometers) and adjust it as needed.
- Data values can be fine-tuned through calibration.
- Users can choose to process data as analog or digital based on their preference.
- They can also decide whether the data should be displayed on the dashboard or limited to reports.
This level of customization removes the previous constraint of supporting only a limited number of parameters or device-specific data. Now, any CAN parameter from any OBDII GPS tracker device can be integrated and processed in TrackoBit without backend modifications.
This update gives users full control over CAN data, making the system more adaptable, scalable, and future-proof. Users are no longer restricted to predefined fields or formats—they have the freedom to define, map, and display data exactly how they need it.
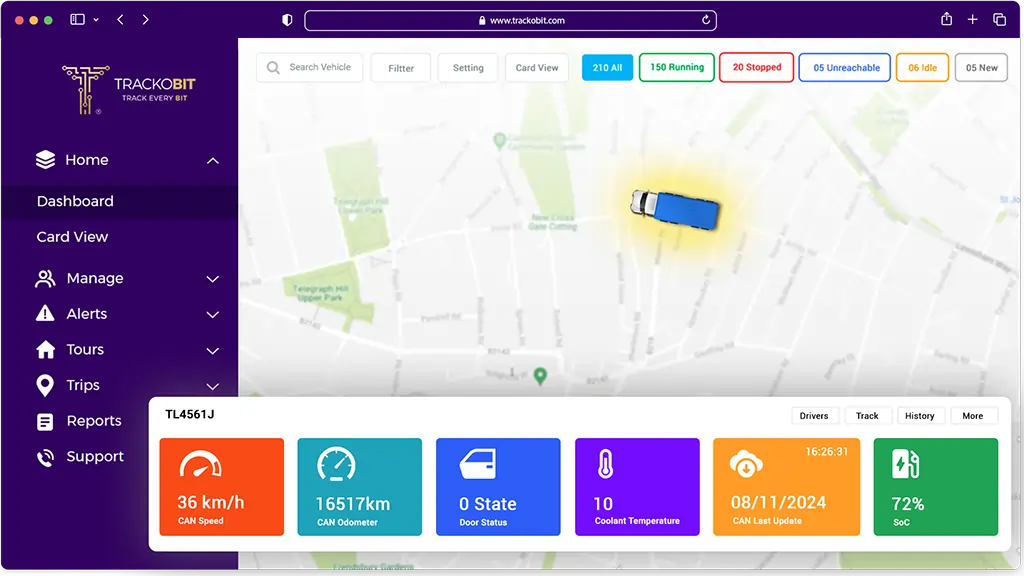
Get refined data for enhanced fleet management.
Conclusion
Smart fleet management starts with smart data. With CAN bus, GPS tracking, and OBD-II working together, managers gain unmatched visibility and control.
TrackoBit’s advanced CAN integration makes it easy to map, monitor, and customize vehicle data. Thus, boosting performance and cutting costs. It’s not just about tracking anymore—it’s about driving smarter!
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Why integrate GPS tracking with CAN Bus data?
Integrating GPS tracking with CAN Bus provides real-time insights into - - Vehicle location, - Engine health, - And driver behavior. This helps fleet managers track performance, improve route planning. Also reduces downtime with predictive maintenance.
-
How does CAN Bus data improve fleet safety and efficiency?
CAN Bus monitors driving behavior, brake response, and seatbelt use. Fleet managers receive alerts for unsafe driving and mechanical issues. This ensures quicker responses and improved driver performance.
-
Can GPS tracking and CAN Bus integration prevent vehicle breakdowns?
Yes, CAN Bus transmits diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and real-time performance data, helping fleet managers detect and fix issues before they lead to breakdowns.
-
What type of data can be extracted from CAN Bus for GPS tracking?
CAN Bus provides data on speed, RPM, fuel level, engine temperature, brake status, and more. This allows GPS tracking systems to monitor vehicle health and driving patterns accurately.
-
Can CAN Bus integration reduce fleet operational costs?
Yes, by analyzing fuel consumption, engine load, and maintenance needs, CAN Bus integration helps reduce fuel wastage, improve efficiency, and cut repair costs.
Tithi Agarwal is an established content marketing specialist with years of experience in Telematics and the SaaS domain. With a strong background in literature and industrial expertise in technical wr... Read More
Related Blogs
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.
-

Plug, Pair, Perform TrackoBit Introduces BLE Sensor Integration
Tithi Agarwal November 26, 2025TrackoBit’s BLE Sensor Integration enables wireless, real-time monitoring with faster installs and accurate insights. It improves fleet efficiency, visibility, and…

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.