-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
How to Execute Accurate and Efficient Hyperlocal Deliveries?
- Author:Drishti Dua
- Read Time:9 min
- Published:
- Last Update: December 9, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
Hyperlocal deliveries have become a common part of society. We are expecting more and more brands to fulfil their orders and execute faster deliveries each day. This system has allowed businesses to create a network that helps them purchase goods from local vendors for delivery.
Table of Contents
Toggle
The past few years, especially after the COVID-19 period, have witnessed a shift in the market. People are more reliant on online shopping than ever before.
But have you ever wondered how this shift could impact the local businesses around your neighbourhood?
Hyperlocal delivery business ideas emerged as a way to tackle this issue. It provides customers with the convenience of receiving goods at their doorsteps without impacting the local businesses offering these goods. The growth of this industry is visible when we look at the growth rate of 14.4% CAGR predicted for the years 2022-2031. This blog will give you an in-depth view of how hyperlocal deliveries are changing the way we shop!
What is Hyperlocal Fulfilment?
Hyperlocal is the term used to describe any activity done ‘locally’. This means that there is a geographical boundary that differentiates which delivery is hyperlocal from the others. This distinction makes understanding hyperlocal deliveries simple
The popularisation of the hyperlocal delivery sector stems from several different factors. But before we dissect hyperlocal deliveries and the trends that have led to making them a household practice, let us first understand the shift in market operations.
Traditionally, shopkeepers fulfilled their deliveries individually. Ads stating delivery options available up to certain kilometres were not hard to come by. But the onset of technology transformed how deliveries get executed and also increased the volume of these deliveries. Customers now have the option to simply order their goods using a smartphone and receive their goods without contacting the seller at all.
Some common examples of hyperlocal deliveries are:
- Grocery delivery
- Laundry services
- Pharmacy
- Food delivery
- Home services
The View of Hyperlocal Fulfilment in the Recent Years
Recently there has been a sudden surge in businesses adopting hyperlocal delivery models. Especially in the pandemic, when people could not go out to purchase basic necessity items like groceries, delivery partners were all they could rely on. Here are some of the observations we can enumerate from understanding this industry expansion:
Factors Behind the Success of Hyperlocal Fulfilment
Companies now deliver products of customers’ choice right to their doorsteps within mere 10 minutes. Who would want to step out of their houses just to purchase bread and milk? This is why a report by the WATConsult’s research division states that there are almost 141 million hypelocal shoppers in India as of 2022. A large chunk of sellers and buyers in this business model deal with FMCG goods.
The success of the hyperlocal delivery industry can be accounted to several factors, some of which include:
- New-age automation technology
- Higher demographic of smartphone users with an internet connection
- Changing preferences of customers
- Improved digitalisation
Retail Business and Hyperlocal Delivery
Retail businesses have been heavily affected by the rise of e-commerce. But hyperlocal delivery systems can become a way to incorporate local businesses with online purchases. Several online shopping platforms work via a network of local businesses. They simply provide these businesses with an online platform and delivery partners. Local shops are responsible for the packaging of these goods which are then handed over to the delivery agent.
E-commerce and Micro-fulfilment
Micro-fulfillment is one of the latest trends in the supply chain industry. The last mile refers to the final stretch in a delivery process, employees taking products from large fulfilment centres to customers. But this step alone can take several days to complete, especially when managed manually. In a world relying on speed, this becomes a pain point for the supply chain. While last-mile automation can reduce the time taken to fulfil orders, it cannot reduce delivery time.
This crisis is the reason why businesses are developing micro-fulfilment centres. Instead of products being stored in large warehouses, they are instead stored in smaller facilities that are more widespread throughout an area. With neighbourhoods having their own fulfilment warehouses, the distance for delivery is marginally reduced.
But why are these categorised as hyperlocal deliveries? That is because executing deliveries originating from such micro-fulfilment centres can be easily completed within 2-3 hours. Geographically, these centres are close to the customers, thus qualifying them on both parameters for hyperlocal delivery.
Read Blog – How to Choose Best Last-Mile Delivery Software?
On-demand Hyperlocal Delivery
As the name suggests, on-demand deliveries rely on the needs and requirements of the customers. They can choose which shop to purchase goods from according to their convenience. Food delivery and express grocery delivery are two of the many popular on-demand delivery models we see in the market.
The gig industry can also be considered an on-demand hyperlocal delivery. Employees provide services like plumbing to their immediate neighbourhood.
What are the Aspects of Hyperlocal Delivery
Hyperlocal deliveries are possible via a series of individual operations. It is only when managers work to optimise each of these steps that we consider the delivery successful. Let us have a look at the various aspects of hyperlocal deliveries:
Demand Management
The process of fulfilling orders and managing inventory differs a lot in hyperlocal deliveries as compared to traditional e-commerce. The prime advantage that hyperlocal businesses have over the brick-and-mortar setup is the control they have over their demands. Businesses affiliated with hyperlocal delivery businesses can choose when and where to stop orders.
ETA Adherence
Time is a huge factor playing in hyperlocal deliveries. The time constraint to even qualify as a hyperlocal delivery margin is within 2-3 hours. Customer satisfaction can take a huge hit with delays to deliveries in this industry. Most delivery apps also share their delivery executive’s ETA with the clients to boost their visibility. This adds pressure on the agent to deliver goods within the shared ETA to maintain a good quality customer experience.
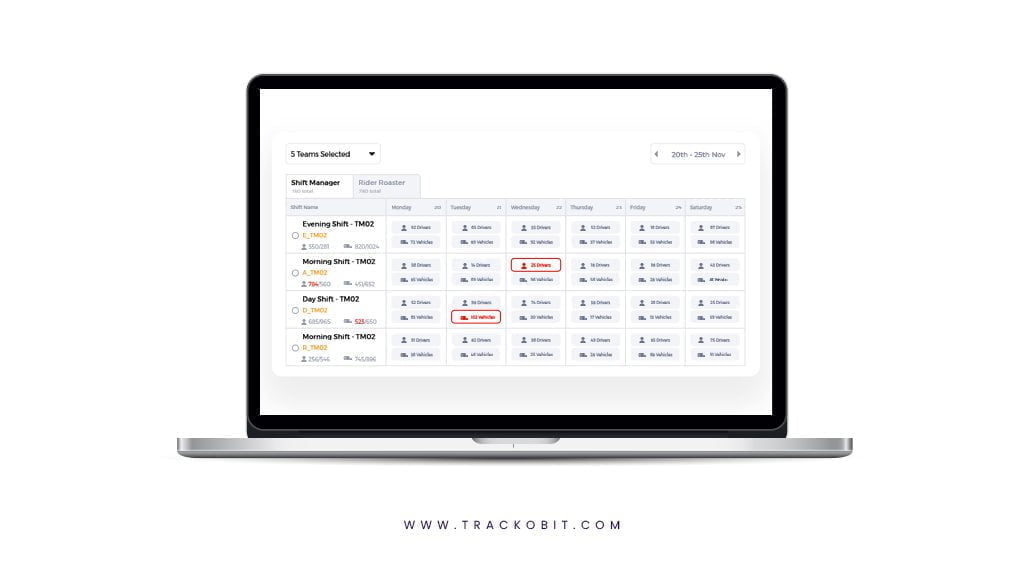
Delivery Scheduling
When there is a workforce working around the clock to complete orders and make deliveries, manual scheduling can cause several issues. There might be an imbalance in the number of tasks that employees receive from their managers. This can not only affect employee retention but also increase delivery times.
As we previously discussed, time sensitivity is the foundation for hyperlocal deliveries, and businesses are now developing their brand around 10-minute deliveries. This is why such issues can affect the brand’s image and deter customers’ trust.
Challenges of Operating a Hyperlocal Business Model
Hyperlocal delivery business models are gaining popularity as we speak. But there are still several operational issues that need resolving for such businesses to thrive. Some of these challenges include:
Inefficient Workforce Management
When there is a surge in orders, the requirement for a workforce also increases. But managing several employees at the same time invites challenges for the business that can affect the business’ overall productivity. Managers need to assign tasks and stay updated on delivery status accurately for the best performance from the employees.
In case of labour shortage, the issue becomes about assigning multiple deliveries to the same person. But this can negatively impact the delivery periods, which can further affect customer satisfaction.
Route Management
One of the reasons for delayed deliveries is inefficient route planning. Inefficiency route planning can disrupt the entire delivery process, once again leading to customer dissatisfaction. Employees can also decide to take smaller but unsafe routes for their deliveries. But any damage sustained to the product, for example, spilt food, can break the business-customer trust.
High Operational Cost
Making quick delivery is not easy and nor is it cheap. After all, the fuel and resources spent on each delivery can add up to a lot of expenditure. Businesses can also lose money if they damage the product entrusted to them for delivery. Not managing orders and formulating multiple delivery trips for deliveries on the same route is also a common way businesses lose their money.
Low Visibility
When out to make deliveries, employees have minimal time to inform managers of their task status. This lack of communication can raise issues for managers as they have no information to further relay to the customer. Manually tracking employees also becomes an impossible task, especially when there are several deliveries happening at the same time.
Emerging Trends in the Hyperlocal Space
The space for growth in the hyperlocal delivery industry is huge. Over the years, we have seen how technology and market requirements have shaped the way businesses operate in this space. But change is never stagnant and neither is the scope of growth for hyperlocal opportunities. For businesses to survive in this competitive industry, it is important that they are well aware of these changes and their business operations accordingly.
Here are some trends that have the potential to change hyperlocal delivery initiatives:
Increasing demand
We mentioned above that the world is now meaning at a fast pace. With this, the patience that customers once had for their orders to be delivered has also reduced. Several brands have marketed and built their brand names for their fast delivery rates, Amazon and Zepto to name a few.
The success that these companies have started a series of startups to emerge in the hyperlocal delivery industry. This influx of demand and the competitive nature of the market does not leave any space for operational errors. Switching companies is as easy as switching from one application to another on their smartphones!
The rising demand has also encouraged popular brands like Zomato to invest in other smaller brands to expand their market. Thus, the company now has businesses dealing with both instant food and grocery delivery.

Growth of last mile technology
The rise of technology means easier and error free operations. Gone are the days when faulty deliveries, damaged goods and time mismanagement were easily acceptable. Last-mile automation means that customers have access to their delivery agents’ locations at all times. In order to grow customer relations, businesses pay extra value to their opinions and complaints.
Investing in last mile delivery software can also help businesses optimise their route planning. The system will help them divide the deliveries on the basis of their area and club together several orders. Thus, boosting time efficiency and also making sure that employees travel only through the most suitable and economical paths.
Gig Economy
Hyperlocal delivery is not restricted to transporting goods from the seller to the customer. It can also refer to a seller providing their services to a client on demand. This can be cleaning the service, installation of electronic devices, maintenance procedures for these devices and so much more. Currently standing at the size of USD 355 billion, this industry is expected to grow at 16.81% CAGR.
These numbers give you an idea of the potential of expanding a business in the gig economy. Redirecting the demand of this industry to the hyperlocal sphere can help companies to expand their clientele. Providing trained people for odd jobs in local areas makes these service deliveries quick, thus falling under hyperlocal delivery standards.
Customisation
Several online delivery platforms provide customers with the option to choose their delivery times. A common example of this can be gift brands like Ferns N Petals and IGP which deliver flowers and cakes for special celebratory occasions. These deliveries often need to happen according to the time decided by the sender. But manually keeping track of these orders and their time slots is a huge window for errors and unsatisfactory deliveries.
Using automation to track orders and schedule deliveries can be a gateway to optimising such hyperlocal delivery services.
Last Mile Delivery Software
Have everything done within second: order sorting, route optimisation, and dispatch planning.
Dont’t believe us?
TrackoMile is Coming Your Way
We mentioned above that automation is one of the rising trends in the last mile and hyperlocal delivery industries. But what if we told you that we have already selected a system that can make your operations all the more efficient?
TrackoMile is a toolkit that can help you track and monitor your delivery agents without having to physically communicate with them every second. The system also allows you to assign them delivery tasks, all clubbed together based on their location. Thus, making the delivery process all the more simple.
So why waste time? Contact our teams of innovators and see how well our system will adapt to your functions and race towards optimisation!
Drishti Dua, a Content Contributor at TrackoBit has a rich background in literature and professional expertise in SaaS and technology writing. She has carved her niche in the space of Geospatial techn... Read More
Related Blogs
-

Top 9 Delivery Management Software in 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 2, 2026By choosing the best delivery management software, companies can benefit from features like route optimization, dispatch management, and more. This…
-

How Rider Tracking Software Improves Delivery Accuracy and Reduces Fraud
Tithi Agarwal December 8, 2025Rider tracking software improves delivery accuracy with real-time GPS visibility and automated ePOD. It also enables route optimisation and fraud…
-
Top Electronic Proof of Delivery (ePOD) Software in 2026
Tithi Agarwal September 25, 2025Electronic proof of delivery has become the backbone of modern logistics. Explore the top 8 ePOD software in 2026 and…
-

3PL vs. 4PL: Which is Best for Your Business?
Tithi Agarwal September 25, 2024Confused about choosing between 3PL and 4PL for your retail supply chain? Read this blog to find out which is…

Subscribe for weekly tips to supercharge your last-mile delivery.
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.