-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What Are Fuel Level Sensors? Comprehensive Guide 2026
- Author:Diksha Bhandari
- Read Time:
- Published:
- Last Update: January 15, 2026
Table of Contents
Toggle
Discover the world of fuel level sensors and their potential to take your fleet management to new heights! Know everything from importance, applications, and types of fuel monitoring devices.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Welcome to the fuel-powered adventure! Today, we’ll dive into the world of fuel level sensors, the unsung heroes that keep our vehicles up and running efficiently.
Fuel expenses eat up the maximum budget allotted to a fleet. On top of it, foes like pilferage, wastage, and leakages make the overall ride all the more heavy on the pockets. This is where fuel tank level sensors come into the picture.
So, let’s rev our engines and embark on this informational journey about fuel tank level sensors!
What Are Fuel Level Sensors?
Fuel sensors or fuel level indicators are ingenious devices installed inside the fuel tank to measure the accurate fuel level in real time. The data is shared with telematics software such as TrackoBit which message the raw data and present the users in a digestible format.
These sensors are further categorised into various types depending on the technology they use to gauge fuel levels. The following section will shed light on them in detail. As far as the use cases of fuel tank sensors are concerned, they help fleet managers:
- Measure fuel consumption patterns
- Plan fuel refills and stops
- Maintain the overall fleet efficiency
- Enhance vehicle and consignment safety.
Applications of Fuel Tank Level Sensors
Where ever the requirement for diesel, petrol or any sort of fuel is there, the application of fuel level sensors exists. Some common domains where fuel sensors are applicable:
- Moveable units – Vehicles, Vessels, Earthmovers, etc.
- Stationary units – Generators, Machines, Fuel Pumps, etc.
Types of Fuel Level Sensors
Having only one option, is even an option? We get you!
Cutting straight to the chase, the following are the common types of fuel level sensors used across industries.
1. Capacitance Fuel Level Sensors
Capacitive fuel indicators come with two electrodes that are immersed at the two ends of a fuel tank. The capacitance between the electrodes changes as the fuel level changes. This change in value is then converted into fuel level readings.
Pros and Cons: The accuracy of capacitance sensors are accurate. They are less susceptible to fuel sloshing and sedimentation. The best part- they are suitable for both liquid and gas fuels.
They are popularly used in vehicles including cars, trucks, vessels, and machines as well.
2. Ultrasonic Fuel Sensors
As the term suggests, the sensors use ultrasonic sound waves to measure fuel levels. They emit sound waves towards the fuel surface, and the amount of time they take to reflect back determines the distance. Hence, the level of fuel is gauged.
Pros and Cons: Contactless measurement of fuel. It’s suitable for fuel tanks of different shapes and sizes. However, the ultrasonic fuel tank level sensor is a little expensive and potential hindrance such as foam may compromise the reading.
These fuel sensors are commonly used in automobiles, boats, and industrial appliances. They come in handy when the instruments have irregular fuel tanks and you require accurate fuel level readings.
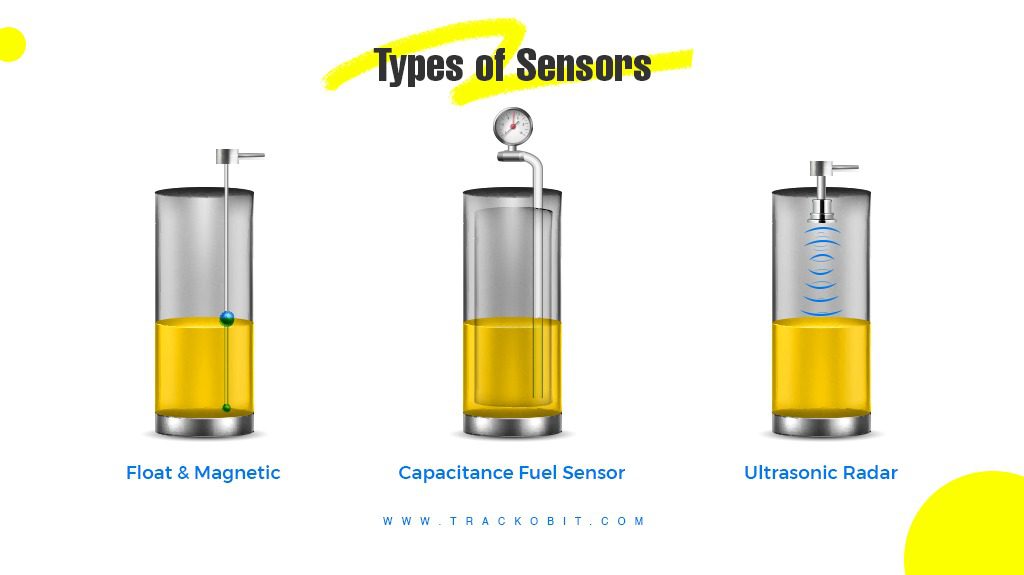
3. Resistive or Float Fuel Indicators
A float is connected to a potentiometer or a variable resistor that moves as the fuel level changes. Hence, the value of resistance also changes, resulting in a change in voltage. The dashboard displays the calibrated value in litres.
Pros and Cons: Its simple design makes it cost-effective and easily compatible with a wide range of fuel management systems. However, its values are not on point and susceptible to flaws due to fuel sloshing.
The resistive fuel tank level sensors are most commonly used in cars, motorcycles and small boats.
4. Magnetic Fuel Tank Sensors
Also, known as Hall effect fuel sensors because they detect the changes in the magnetic field called the Hall effect. The sensor detects the change in fuel level when the change in magnetic fields is recorded.
Pros and Cons: Hall-based sensors offer accurate and non-contact fuel measurement even in asymmetric fuel tanks. Its higher cost and limited compatibility with most fuel types are its downsides.
Applicable mainly in industrial fuel systems where compatibility with corrosive fuels is required.
Benefits of Fuel Level Sensors in Optimising Fleet Operations
One of the primary and most popular applications of fuel sensors is in automotive vehicles. In the fleet of commercial vehicles, where optimising each and every aspect of operations is a must to draw a profitable bottom line, petrol-level sensors prove to be a game changer.
Let’s elaborate on the benefits of fuel sensors!
1. Improved Fuel Management
Real-time, as well as historical data, enable automatic alerts such as fuel refill reminders, fuel leakage, pilferage or abnormal fuel drainage. Advanced fleet management software also provides a list of nearby fuel stations and current fuel prices in different states, allowing fleet managers to plan fuel refilling stoppages accordingly.
2. Increased Vehicle Efficiency
With real-time and accurate fuel level updates, drivers and managers can make informed decisions pertaining to fuel refilling, vehicle health, and trip planning. If certain vehicles are consuming more than usual fuel, it means either the vehicle needs servicing or the driver is not practising eco-driving. Spotting such anomalies and correcting them at the right time improves overall fleet efficiency.
3. Enhanced Safety
Abnormal fuel drainage may be the result of leakage, which is not safe for the vehicle and consignment can be detected by fuel level sensors. Unannounced route deviations breed fuel pilferage which can be detected with a win-win combination of route deviation alerts and fuel monitoring reports. This is where the heroism of fuel-level sensors comes into play.
4. Cost Savings
On-point and detailed fuel reports help in analyzing fuel efficiency, determining areas of improvement, and making insightful decisions regarding fuel procurement, vehicle selection, and operational strategies. Driving behaviour monitoring, planning routes and analyzing their impact on fuel consumption helps save fuel wastage. These measures improve overall fuel and fleet costs.
5. Reduced Downtime
Unpredictable fuel runouts may lead to unnecessary downtime and negatively impact customer satisfaction. Always stay at the forefront of optimal fleet management with live updates. Overlooking possible vehicle ailments, bad driving practices, and route planning is not an option with fuel level sensors analyzing the direct impact on fuel consumption.
6. Lesser Stress on the Environment
Fuel sensors indirectly help in environmental sustainability. Reduction in fuel usage means lesser emissions of carbon footprints. Ignorance is bliss and reality is heartbreaking! When carbon emissions take the shape of numbers, then only do we realise our wrongdoings.
How Fuel Level Sensors Work
To keep it short and precise, the fuel sensors work in four simple steps. These steps include installation, function based on their respective principles, the transmission of data, and then the final output.
Let’s discuss the entire procedure in detail.
1. Sensor Placement
Before the technology and the device work as expected, it’s important to check the compatibility of the fuel sensor with the software. After the device gets a nod from the IT team, the sensor is installed in the fuel tank.
The exact placement of the fuel monitoring device may vary depending on the fuel system and vehicle/fuel tank design. The sensor is strategically placed to draw accurate readings.
2. Sensor Operation
After the sensor is mounted, it starts operating on its respective principles such as resistive, capacitive, ultrasonic or magnetic. The sensors detect the fuel level in their respective units.
3. Signal Processing
The information received by the sensor pertaining to fuel levels is then converted into an electrical or electronic signal. The signals get recorded either in voltage, resistance, capacitance or frequency. The recorded signal is then sent to the software via the cloud.
4. Data Output
The readings or reports on fuel that we see on our phones or web portals are the processed version of the data received by the software. As per the calibration, the fuel level readings may appear in the form of fuel charts, tables or graphics.
Keep Your Fuel Data
Accurate!
Download TrackoBit’s expert guide to
fuel sensor maintenance and calibration
for smoother ops & zero guesswork.
Fuel Tank Sensor Calibration
Calibration of fuel sensors or tanks is important to adjust the device’s readings to accurately measure and reflect the fuel levels on the dashboard. Fuel calibration is important because factors such as disparity in fuel density, sensor drift, and installation variations can affect the values. Therefore, to avoid inaccuracy of data and wrong business decisions pertaining to fuel management, calibration is crucial.
| In measurement technology and meteorology, calibration is the process of adjusting and aligning the measurement of instruments(in this case fuel tank sensors) to match a defined reference or standard, ensuring accurate and precise readings. |
Fuel Level Calibration Procedure
The calibration process for most fuel monitoring systems is more or less the same. In the commercial space, most of the fleet techniques use the following technique to calibrate fuel.
Step 1: Measure and pour the stipulated volume of fuel into the fuel tank, referred to as a “pass.” Ideally, a pass is 1/10th or 1/20th of the tank volume. This ensures enough entries on the calibration table.
| If the total tank volume is 20 liters then each pass of 1/10th will amount to 2 L. This means there will be 10 readings on the calibration table. You can use transfer pumps to measure the exact volume of the pass. |
Step 2: Record the reading received either in voltage, resistance, frequency, etc. corresponding to the pass value (measured in liters or gallons) in the calibration table.
Step 3: Repeat the process as you keep adding the passes and the fuel level sensor keeps changing the value.
Step 4: If the tank has an irregular shape, adjust the pass volume by dividing it by two as you reach the asymmetrical area of the tank.
Step 5: Define and feed these values of the calibration table on the Fleet management software you use and test the fuel monitoring for data output.
Tips For Accurate Calibration:
|
Fuel Monitoring By TrackoBit
A good sensor becomes the best when it joins forces with intelligent software. TrackoBit’s advanced fuel monitoring solutions bring out the best fuel monitoring solutions.
TrackoBit allows remote fuel monitoring in a few clicks. Once the sensor is integrated with the software and the calibration is done, you are good to go.
Offerings of Our Fuel Monitoring System
1. Real-time Fuel Level Update
Our fuel monitoring system delivers real-time fuel level updates on each vehicle in the fleet. The real-time visibility into such data helps fleet managers make instant business decisions confidently.
2. In-depth Fuel Report
Analyse fuel consumption patterns with the help of insightful reports on fuel average, refill, and drainage. Fuel charts display absolute mileage with respect to speed, ignition on/off, distance travelled, etc. You get trip-wise, vehicle-wise, and driver-wise fuel reports for better analysis.
3. Instant Notifications
Get live notifications and alerts every time fuel levels drop/rise instantly or abnormal fuel consumption patterns are detected. The software shares notifications/alerts via SMSs, WhatsApp messages, push notifications or emails.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fuel Level Sensors
-
How do I reset my fuel level sensor?
Resetting the fuel gauge in the vehicle is completely different from resetting the fuel tank level sensor in a commercial fleet. If we talk about resetting the fuel tank sensor, it simply means recalibrating the sensor readings. In case there is an error code from the software’s point of view then fix it before recalibrating.
-
Can I get fuel level readings on the software dashboard with an external fuel level sensor installed in the vehicle?
Yes, with the help of OBD CANBus data, it is possible to derive the fuel level readings from the central unit of the vehicle.
-
Where is the fuel level sensor located?
The fuel tank level sensor is located inside the fuel tank as it has to measure the fuel level at all times. However, the exact position of the installation may vary from the type of vehicle to the type of sensor used.
Diksha Bhandari is the Content Marketing Manager at TrackoBit. With over a decade of experience in the media and advertising industry, she has transitioned her expertise to the world of software and t... Read More
Related Blogs
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.
-

Plug, Pair, Perform TrackoBit Introduces BLE Sensor Integration
Tithi Agarwal November 26, 2025TrackoBit’s BLE Sensor Integration enables wireless, real-time monitoring with faster installs and accurate insights. It improves fleet efficiency, visibility, and…

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.