-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
What is a Commercial GPS Tracker And How Does it Work?
- Author:Anvesha Pandey
- Read Time:8 min
- Published:
- Last Update: May 16, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
Planning to invest in a GPS Tracker? This guide covers everything from how they work to the different types available. Learn what features to look for and make an informed decision.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Readers, did you know!
The reports of the GPS Industry Council state that the global GPS tracking device market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2019. It is projected to grow by over 15% annually, reaching around $7.6 billion by 2025.
Do you wonder why we see such a huge hike in the numbers? What does a GPS tracker do?
At its core, a GPS tracker tells you exactly where something is in real time. But it’s not just about finding lost items. These devices are revolutionizing industries from logistics and fleet management to personal safety.
However, many businesses still grapple with challenges related to asset theft or misplacement, unplanned routes, and operational efficiencies. So together let’s unfold how GPS trackers mitigate such challenges, what actually it is their types, working, and more.
What is a Commercial GPS Tracker? – Basics First
A commercial GPS tracker is a device businesses use to monitor the real-time location and movements of their vehicles, assets, and consignments. The trackers use a combination of GPS technology which further helps in determining location and cellular networks to transmit this to a server or a fleet management system.
The primary purpose of commercial GPS trackers includes real-time tracking, better security, enhanced visibility, and more.
Various types of GPS trackers are available in the market, such as Vehicle GPS trackers (like OBD trackers, and hardwired trackers), assets GPS trackers (portable trackers, elocks), and more. For more advanced location tracking and sourcing of vehicles, fleet managers often make their bet on popular GPS models such as Teltonika FMB124, Gosafe GIC, Quecklink, etc.
Before we get into the detailed workings of GPS trackers, we need to understand their various components and the role each of the components plays.
📌A Must Read- How to Choose the Right GPS Trackers in 2025?
What are the Components of GPS Trackers? A Deep Dive
GPS trackers are made up of several key components that work together to provide accurate real-time locational data, speed, route history, vehicular movements, and other related data.
The various components of GPS trackers include a GPS receiver, microcontroller, GSM/GPRS module, battery and power supply, and an antenna.
- GPS Receiver- This particular component helps in receiving signals from at least four GPS satellites to determine the device’s precise location.
- Microcontroller- This device helps process the data from the GPS receiver and manages the overall operation of the device, including handling communication with other components and external devices.
- GSM/GPRS Module- This helps send locational data, speed, and other information to a server or a designated recipient via cellular networks.
- Battery/Power Supply- As the name suggests, it helps in providing power to the device. It can either be with the help of a rechargeable battery or a direct connection to a vehicle’s power supply.
- Antenna- The antenna helps ensure good signal reception for both GPS and cellular communication.
How Does A GPS Tracker Work? – Technical Functioning
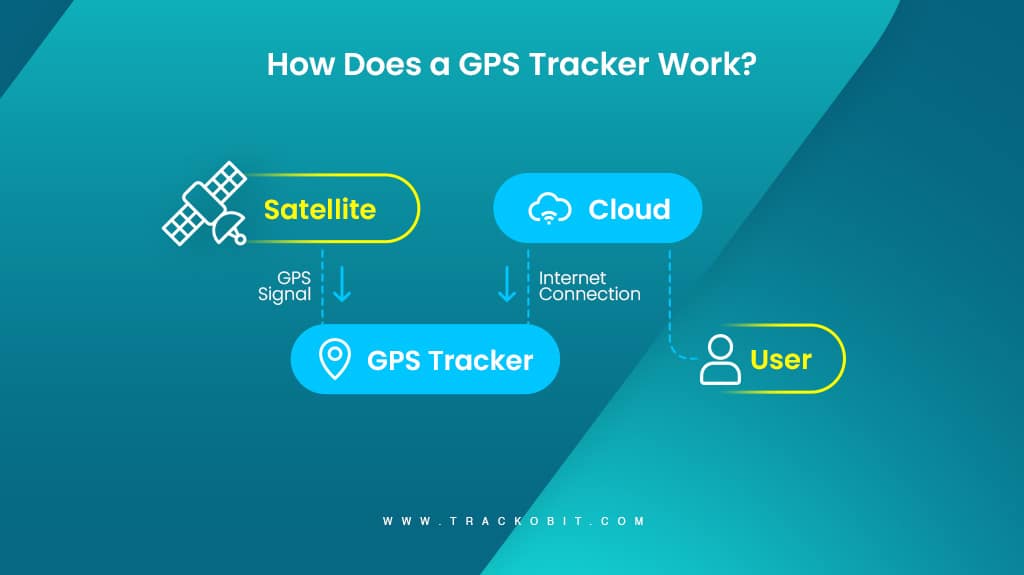
Now that we know the components of the system, let’s learn how these components work together to provide you with real-time locational data.
STEP 1 – Signal Reception
The GPS receiver in the tracker continuously looks for signals from a network of satellites. Each satellite broadcasts a signal that includes the location and the precise time the signal was sent.
Step 2- Triangulation
The GPS receiver calculates the distance to at least four satellites to determine its location through a process called triangulation. This involves measuring the time it takes for the signals to travel from the satellites to the receiver.
Step 3- Data Processing
The microcontroller processes the location data and prepares it for transmission. This includes data like speed, direction, time, and location.
Step 4- Data Transmission
Once the data is processed, The GSM/GPRS module sends the processed data to a remote server or a recipient (for instance a fleet management software) with the help of cellular networks. This transmission can occur in real-time or at scheduled intervals.
Step 5- Data Storage
Now that you have started receiving data, for sure this data needs to be stored somewhere. So the received data is stored on the server and can be accessed by users through the web. This allows for real-time tracking, historical data analysis, geofencing, and more.
Okay so now that you know how GPS trackers technically work, let’s look into some of the popular kinds of GPS trackers.
What are the Different Types of GPS Trackers? – A Detailed View
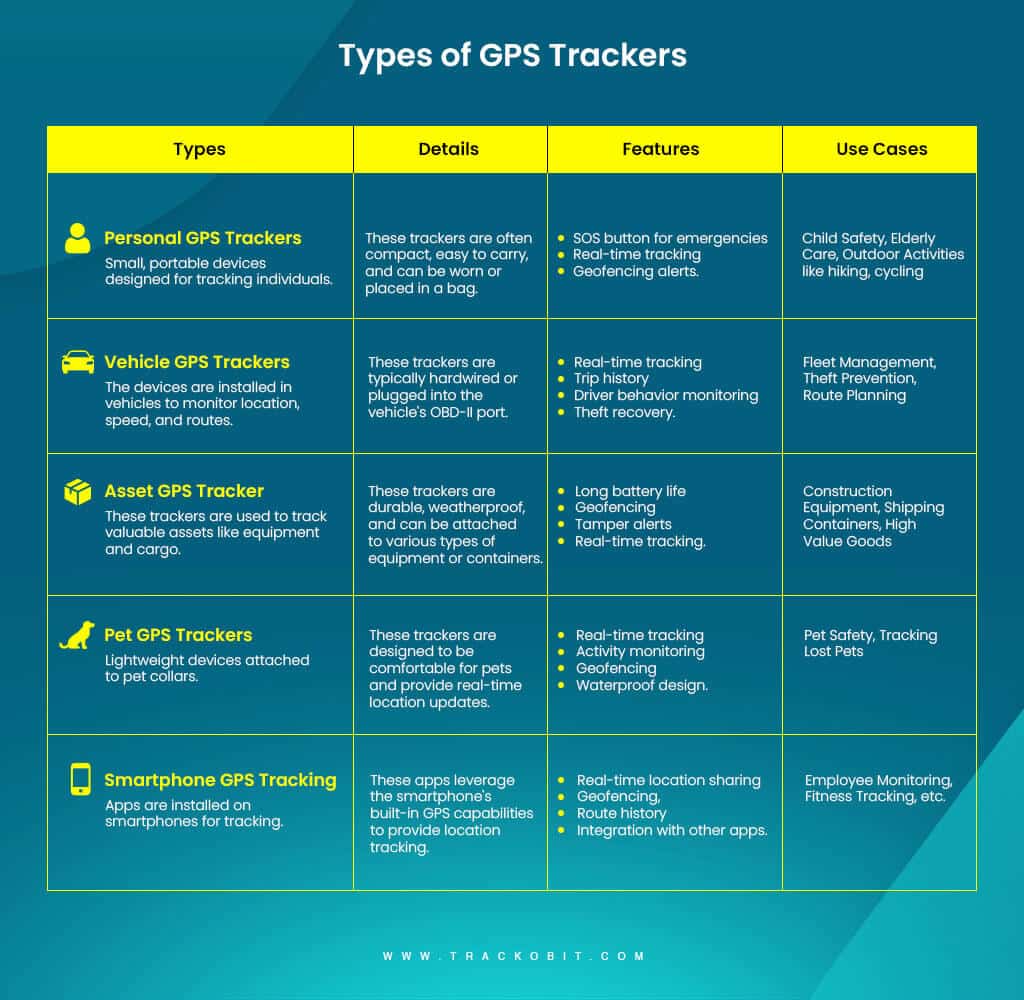
Okay so let us tell you there are several types of vehicle GPS trackers available in the market. Each is designed for specific applications and use cases.
Let’s unfold the 5 types of GPS trackers.
✅ OBD Trackers
OBD (On-Board Diagnostic) trackers are plug-and-play devices that are connected to the vehicle’s OBD-II port. These trackers are very easy to install and provide real-time locational tracking along with diagnostics information like engine status, fuel level, and locational information.
These trackers are mostly used in fleet management and personal vehicle tracking. It is because these GPS trackers are convenient to use and also they can offer detailed insights into vehicle performance, and health.
Must Read: What is OBD2?
✅ Active GPS Trackers
Active GPS trackers aka real-time GPS trackers. These trackers continuously collect and transmit locational data to a central server using cellular networks. This allows for real-time monitoring and immediate access to the tracker’s current location, i.e., minute-to-minute location updates.
Active GPS trackers are ideal for constant tracking, such as monitoring delivery vehicles, tracking valuable assets, or ensuring the safety of individuals.
✅ Passive GPS Trackers
Passive GPS trackers, also known as data loggers, store location data instead of transmitting it in real-time. This data can be downloaded and analyzed when needed.
These trackers are often used for documenting travel routes, mileage tracking, and monitoring vehicle usage patterns without the need for constant internet connectivity.
✅ Hardwired Trackers
Hardwired Trackers are permanently installed in a vehicle by connecting directly to its electrical system. They offer a more reliable and tamper-resistant solution compared to plug-and-play trackers.
These devices are often hidden to prevent unauthorized removal or breaking of the trackers. These are commonly used in fleet management, theft recovery, and long-term vehicle tracking applications.
✅ Asset GPS Trackers
Asset GPS trackers are designed to monitor and protect valuable assets such as equipment, containers, and shipments. These trackers can be portable or fixed and often come with extra features like tamper alerts and environmental sensors to monitor conditions such as temperature and humidity.
Asset GPS trackers play a huge role in logistics, construction, and any industry where tracking the location and status of assets is essential for operational efficiency and security.
📌Have a closer look at the different kinds of GPS Trackers – 6 Types of Vehicle GPS Trackers – For Fast & Accurate Tracking
What are the Applications of Commercial GPS Trackers?
Well, commercial GPS trackers cover a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common applications of GPS trackers are unfolded below –
Fleet Management
Commercial GPS like Teltonika FMB125 is widely used in fleet management to monitor the real-time location, speed, and routes of the vehicle. They help optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, ensure timely deliveries, and improve overall operational efficiency. Moreover, fleet managers can also track driver behavior, schedule maintenance, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Asset Tracking
When it comes to industries like construction, logistics, and manufacturing, GPS trackers are widely used to monitor the location and status of valuable assets such as machinery, containers, and shipments. Eventually, the trackers help prevent theft, streamline asset utilization, and ensure that assets are available when needed.
Theft Recovery
GPS trackers (like elocks) are powerful tools for recovering stolen vehicles, equipment, and other valuable assets. Enforcement agencies or fleet businesses can quickly locate and recover stolen items by providing real-time location data. This application is particularly valuable for car rental companies, heavy equipment owners, and individuals with high-value personal property.
Delivery & Logistics
When we talk about the delivery and logistics sector, GPS trackers help monitor and manage the movement of goods from warehouses to end customers. They ensure timely deliveries, optimize delivery routes and provide real-time updates to customers.
This improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances customer satisfaction by providing accurate delivery times and tracking information.
Personal Safety & Monitoring
Personal GPS trackers are used for the safety and monitoring of individuals, such as children, the elderly, and employees working in remote or hazardous locations. These trackers can provide real-time location updates, emergency alerts, and geofencing capabilities to ensure the safety and well-being of the wearer.
They are also used in lone worker protection and outdoor activities like hiking and trekking.
Parting Words
Well, now we are all set to end this piece, we have covered almost all the ins and outs of GPS trackers. By now you would surely have understood that this investment in your fleet can bring you wonders.
While GPS trackers are powerful tools, they truly shine when combined with robust GPS vehicle tracking software like TrackoBit. Together, they form a dynamic duo that can revolutionize your operations. And the best part? Our solutions are compatible with a wide range of GPS trackers available in the market.
So, ready to unlock the full potential of your fleet?
FAQs
-
What is GPS tracking for Commercial Vehicles?
GPS tracking for commercial vehicles involves using Global Positioning System (GPS) technology to monitor and manage the real-time location, movement, and status of vehicles in a commercial fleet. This technology helps fleet managers optimize routes, improve fuel efficiency, track driver behavior, ensure timely deliveries, and enhance overall operational efficiency. It also provides valuable data for maintenance scheduling, compliance with regulations, and improving customer service.
-
What is the future of GPS tracking?
The future of GPS tracking looks promising with advancements in technology and increasing integration with other systems. One significant trend is the integration with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which will provide more comprehensive data and enable greater automation. Additionally, the incorporation of AI and machine learning will facilitate predictive analytics, smarter route planning, and automated decision-making, leading to more efficient and effective tracking solutions.
-
How to use a GPS tracker?
To use a GPS tracker, Install the tracker according to the type: plug-and-play for OBD trackers, hardwiring for permanent setups, or simply placing portable trackers with the asset. Activate the tracker by setting up an account with the service provider and linking the device. Configure settings like geofences, alerts, and reporting intervals through the tracking platform. Monitor real-time location, review historical data, and receive alerts via the web or mobile app. Finally, use the collected data to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and improve security.
-
How does GPS tracking work?
GPS tracking uses a satellite network that sends signals to a GPS receiver. The receiver calculates its exact location (latitude, longitude, and altitude) by triangulating the signals from at least four satellites. This data is then transmitted to a central server via cellular or satellite networks, allowing real-time tracking of the device's position.
-
How to track a vehicle?
To track a vehicle, choose a GPS tracker like an OBD tracker, hardwired tracker, or portable tracker. Install it by plugging it into the OBD-II port or connecting it to the vehicle’s electrical system. Activate the tracker by setting up an account and linking the device, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Use the web or mobile app to see the vehicle's location in real time, set up alerts, and view reports. This helps you monitor the vehicle, find better routes, and improve overall management and efficiency.
Anvesha is a communication specialist at TrackoBit. With a strong background in media and communications, she adds much-needed balance and brevity to TrackoBit’s... Read More
Related Blogs
-

5 Best Driver Behavior Monitoring Systems for 2026
Tithi Agarwal February 23, 2026Having the best driver behavior monitoring system is a necessity as it helps you ensure driver safety and optimize operational…
-

Why is Driver Drowsiness Detection System Important for Fleet Management?
Shemanti Ghosh February 4, 2026A driver drowsiness detection system is critical for fleet management. It helps prevent fatigue-related accidents and reduces operational risks through…
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.