-
TrackoBit
Manage commercial vehicles with the new-age Fleet Management Software
TrackoBit -
TrackoField
Streamline your scattered workforce with Field Force Management Software
TrackoField -
Features Resources
-
Blog
Carefully curated articles to update you on industrial trends. -
White Paper
Insightful papers and analysis on essential subject matters. -
Glossary
Explore an alphabetical list of relevant industry terms. -
What’s New
Get TrackoBit & TrackoField monthly updates here. -
Case Study
Explore the cases we solved with our diverse solutions. -
Comparisons
Compare platforms, features, and pricing to find your best fit.
-
About Us
Get to know TrackoBit: our team, ethos, values, and vision. -
Careers
Join the most dynamic cult of coders, creatives and changemakers. -
Tech Support
Learn about our technical support team and services in detail. -
Events
Check out the exhibitions where we left our marks and conquered. -
Contact Us
Connect with us and let us know how we can be of service.
How Will 5G Impact Vehicle Telematics?
- Author:Ayushi Nagalia
- Read Time:7 min
- Published:
- Last Update: December 9, 2025
Table of Contents
Toggle
The future of telematics lies in interconnectivity and cross-networking. So yes, if you’re wondering Will 5G Impact Vehicle Telematics – it will! 5G will completely transform how vehicles and telematics systems will operate in the future!
Table of Contents
Toggle
Mobile networks have been on a roller coaster since the 1980s when 1G came out. The current best 4G offers download speeds up to 100Mbps. However, 5G will offer 10 times the current highest speed while connecting 50 to 80 million devices globally by 2025.
Vehicle telematics relies on mobile network download speed. The more vehicles connected to the Internet, the better their communication will be. This communication will enable better telematics. Thus, 5G will bring some exciting changes in the vehicle telematics realm and we’re all in for it!
Understanding the Network Maestro: What is 5G?
Since 1973 each mobile network generation has served decadal, societal, and market requirements. 5G, or the fifth-generation mobile network, is the next technological breakthrough designed to connect the world seamlessly.
5G functions on two frequency ranges: FR1, functioning on bands below 7.123 GHz, and FR2, inclusive of the mmWave spectrum of 52.6 GHz or higher frequency bands. However, when 5G includes frequency bands higher than 100 GHz according to plan, it will be a leapfrog from the current networks.
1G focused on analog voice, 2G on digital voice, 3G introduced mobile data, and 4G popularized mobile broadband. However, unlike the previous mobile network generations, 5G does not have isolated concerns. Through a unified air interface, 5G will connect 100 times more devices to build an ultra-fast and low-latency IoT ecosystem.
5G: The Speed Supersede
5G has ultra-low latency, high reliability, massive network capacity, higher peak data speeds, and increased availability capacities. All this can be channeled into telematics, augmented reality, virtual reality, UHD video streaming, and smart home management tech.
5G enables the ambitious growth towards stronger IoT infrastructures and automated telematics with its unimaginable speed. It offers 10 GBPS of speed, which is 100 times faster than 4G LTE network at 1,000 Mbps speed. Similarly, 5G offers low latency of 1 millisecond, superseding 4G’s 200 milliseconds latency.
To put things into perspective, a 5G connected vehicle will have a reaction time 250 times faster than humans. Moreover, in a single day, it will be able to upload the OBD data 4G takes 100 days to upload.
Challenges to 5G Implementation
5G is expected to become the cornerstone of next-gen telematics and autonomous vehicles. Its ubiquitous connectivity will pave the way for future automobiles and fleet management systems. However, it is not completely bulletproof of implementational challenges.
-
Virtual and Agile Network
Unlike the previous generations, 5G doesn’t build upon the existing physical network infrastructure. Instead, 5G will be completely cloud-native. Its Network Function Virtualization and Software Defined Networking (NFV and SDN) foundation will turn physical networks into eSIMs and clouds. However, a cloud-native network will pose the challenge of higher cyber security risks and maintaining network identity.
-
Connecting Machines
All previous networks connected people while 5G will connect machines. The Ericsson Mobility Report estimated about 2.2 billion devices to be connected to 5G by 2024, most of which will have nothing to do with telecom.
While connecting such a large variety of devices, 5G will have to adapt to each device’s varied bandwidth requirements. This is because some devices need low bandwidth over short distances while others need high bandwidth bursts over long distances.
-
Data Privacy
5G will be completely virtual, making it vulnerable to cyber attacks and compromising data privacy. Cyber Attackers will have multiple entry points into the virtual data network. Since all data will be stored on the ‘edge’ instead of being stored centrally, the increased number of connected devices will cause data privacy issues.
-
Increasing Demands
Other than just mobile devices and vehicles, 5G will connect a massive number of dedicated and general utility devices. From a huge density of connected devices, sensors, vending machines, and wearables, the quantum of ‘online’ vehicles will only increase in the future. This might create cross connectivity and low supply issues.
How Will 5G Impact Vehicle Telematics To Drive Connected Cars?
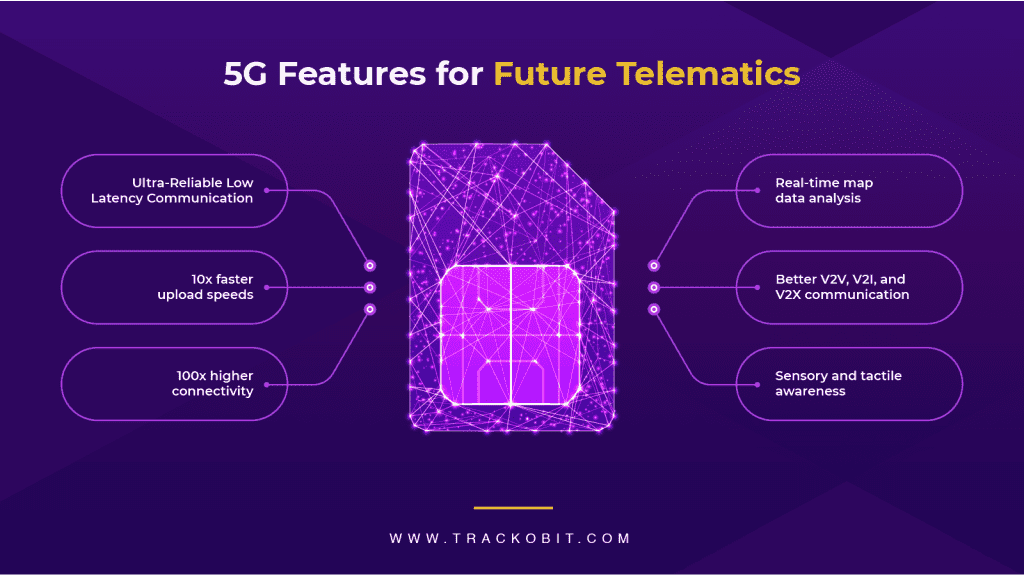
Connected cars begin from IoT and telematics and result in self-driving and completely automated vehicles. The future of the automotive industry lies in 5G and its low latency, high speed, and phenomenal reliability. 5G acts as the missing piece in the complex IoT architectural puzzle slowly migrating towards facilitating level 3-5 automated cars.
-
Low Latency and High Speed
5G enables ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC). It transforms applications like virtual/augmented reality and autonomous vehicles that rely on low latency.
The newest mobile network can achieve less than 1-millisecond latency with 99.9% mmWave uplink and downlink reliability. This paves the path for automation by letting sensors ‘talk’ to one another in real-time.
With 4G’s speed and latency, LIDARs, cameras, lasers, and sensors cannot communicate well enough to substitute human ears, eyes, and tactile senses. However, with 5G, vehicle response can become 250 times faster than human reflexes.
According to ctia.org, wIth 5G’s URLLC, a connected car running at 60 mph will move only one inch on sensing an obstacle. However, 4G’s latency will allow it to move 4.6 feet after obstacle sensing, which is enough distance for the vehicle to collide.
-
Connectivity for Safety
Level 3 automated cars are unpopular because of the market’s apprehension about their safety. However, 5G’s connectivity and low latency play a huge role in safeguarding automated vehicles.
4G supports safety sensors such as cameras, proximity sensors, LIDARs, and SOS buttons. However, when 5G allows the sensors to interact with one another in real-time, telematics’ scope expands to V2X (Vehicle to Everything) communication.
Through V2X, vehicles are not restricted to the designated software. They can delve into Vehicle to Infrastructure (V2I), Vehicle to Pedestrians (V2P), and Vehicle to Vehicle (V2V) communication. Such communication when paired with URLLC makes the vehicle omniscient of its surroundings in real-time. According to NHTSA, V2V and V2I connectivity can obviate the seriousness of about 80% of non-impaired crashes.
The network’s zero-failure reliability and ultra-low latency create a failure proof toolkit for connected and automated vehicle security. Through this toolkit, 5G offers ADAS systems such as forward collision warning, intuitive parking sensors, emergency braking, do-not-pass warning, blind spot sensing, and left turn alerts.
-
Inclusive and Real-Time ETAs
Without 5G’s holy trinity of speed, reliability, and low latency, ETAs have only been statistical and not live. However, 5G’s superior connectivity can operate 1 million devices per square kilometer. Therefore, even in densely populated areas, 5G offers live ETAs.
Not all of these devices are general utilities such as vehicles. In fact, with so many devices online, most of them are specific-utility such as vending machines, ATMs, etc. Therefore, through V2X, V2V, and V2I connectivity, ETAs can be more accurate than ever.
Unlike with 4G, 5G-powered fleet management software will not function on time, distance, and speed calculation to generate ETAs. Now, ETAs will be generated in real-time keeping road conditions, traffic estimates, weather conditions, and other external factors in calculation.
The connected car’s ETAs will be accurate from the trip’s commencement till the end. When destination geocodes are entered into tracking software, 5Gs superior speed and connectivity will communicate with all sensors and devices online on route and calculate real-time ETAs.
-
Video Telematics
The future lies in data so data should be collected from as many resources as possible. 4G’s mobile broadband facilitated the black box technology that allows fleet managers to get insight into their vehicle’s functioning.
Nascent video telematics includes one or two cameras monitoring driver behavior. However, with 5G’s move towards automation, video cameras can help generate stronger map data, facilitate real-time navigation, strengthen V2X communication, and reduce road collisions.
Video analysis of on-road vehicles along with AI will improve road predictive and prescriptive maintenance and safety.
Sending video data from vehicles to software in real-time also allows for smoother operations and accident management for fleet managers. 5G’s superior connectivity allows all vehicles to be connected on one front with negligible latency so that the fleet can be operated as one.
-
Enhanced Fleet Management
The more the data and the lower the latency networks have, the better the fleet management software will function. 5G’s next-gen speed and up data transfer along with 100x connectivity allows fleet management software to become a beacon of information and efficient functions.
Through V2X communication, route planning software will be able to communicate emergency route situations such as traffic, accidents, and unmanageable weather conditions. Without delays and downtime, this V2X communication might seem as faultless as if the devices and sensors are speaking with one another in real-time.
Fleet management systems will also have enhanced and inclusive route planning systems. The software will take only a few seconds to reroute through unplanned hurdles and communicate that change to the entire fleet.
Vehicle maintenance will not only run on premeditated schedules but also according to vehicle conditions. Therefore, when sensors detect issues in part of the vehicle, drivers will be notified within seconds.
-
Automated Vehicles
Everything 5G stands for is automation and complete vehicular awareness. 5G aids vehicles to be completely aware of their surroundings through numerous sensors sharing information in real-time.
Autonomous vehicles have stopped being a piece of fiction and are slowly coming to life. Self-steering and slightly connected Level 1 and 2 cars have moved from being luxurious products to premium ones.
Until now, most semi-autonomous vehicles function on V2V communication through a software medium for data transfer. However, with the advent of 5G, V2X communication will come to life and therefore, vehicles will be absolutely aware of their close proximity.
5G is the stepping stone to ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems). Through 5G’s data-pipeline, massive amounts of data being transferred within the IoT infrastructure allows ADAS to be intuitive and adoptable.
As Harman’s VP of Telematics Vishnu Sundaram mentioned, 5G is the stepping stone that will allow Level 3 to 5 automated cars to become a tangible reality through sensor detailing of map data.
Parting Words
The technical world is slowly making everything that we admired in movies a reality. Very soon, we will get to see self-driving cars available in the market, regardless of their exclusivity. However, regardless of the techniques engineers come up with, only high-capability mobile networks such as 5G make execution possible.
5G is set to create a global network of devices functioning 100 times faster than the existing 4G LTE connections. Complete 5G connectivity will improve peer-to-peer communication and will enhance vehicle telematics. Lower latency and higher speed will pave a new path for futuristic and more reliable fleet management systems!
Ayushi Nagalia is a Senior Content Specialist at TrackoBit. She is a marketing maverick with a lush background in literature. With years of experience crafting content for various niches, she speciali... Read More
Related Blogs
-

When Tracking Needs a Clock: Rethinking Fleet Visibility
Tithi Agarwal December 24, 2025Read on to understand why fleet tracking works better when it follows working hours. Because visibility should support operations, not…
-

What Makes TrackoBit’s Video Telematics Software Truly Next-Gen?
Shemanti Ghosh December 17, 2025TrackoBit’s video telematics software blends smart video intelligence with full server control. The result? Superior fleet reliability and safety.
-

Plug, Pair, Perform TrackoBit Introduces BLE Sensor Integration
Tithi Agarwal November 26, 2025TrackoBit’s BLE Sensor Integration enables wireless, real-time monitoring with faster installs and accurate insights. It improves fleet efficiency, visibility, and…
-

How to Use Driver Behavior Reports as a Sales Hook to Close Big Fleets
Tithi Agarwal October 16, 2025TrackoBit’s driver behavior reports empower fleet providers to win big contracts by showcasing safety, efficiency, and measurable ROI.

Subscribe for weekly tips to optimize your fleet’s potential!
Your inbox awaits a welcome email. Stay tuned for the latest blog updates & expert insights.
"While you're here, dive into some more reads or grab quick bites from our social platforms!"Stay Updated on tech, telematics and mobility. Don't miss out on the latest in the industry.
We use cookies to enhance and personalize your browsing experience. By continuing to use our website, you agree to our Privacy Policy.